INTEGRATIVE KETOGENIC DIET

WARNING: Side effects may include lower levels of stress and anxiety, increased productivity, higher sex-drive, drastic increase in functional lifespan, better memory, and a more pleasant personality.
As an Amazon Associate―#CommissionsEarned
CONTENT
To have health, first ask yourself if you are willing to remove what is causing your illness; only then will it be possible to find solutions.
Solutions providing coherent information with nutritional knowledge for the task of regaining and maintaining health, beauty and happiness.


If you present any of these symptoms:

Form, Function & Beauty
- Acanthosis Nigricans
- Achy Joints
- ADHD (Attention Deficit Hhyperactivity disorder)
- Alopecia Areata (hair loss)
- ALS (A myotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) or Lou Gehrig's disease
- Alzheimer's
- Amyloid Deposits
- Anxiety
- Arthritis-like joint pains
- Asthma
- Ataxia
- Atrial Fibrillation Arrhythmia
- Autism
- Autoimmune disorder
- Behcet's Disease
- Bipolar disease
- Baldness
- Brain Tumors, Injury or Surgery
- Carbohydrate Intolerance
- Cancer
- Cancer of the Mouth, Throat or Esophagus
- Cancer of the Large Intestine, Hepatobiliary system (liver and bile ducts) and Pancreas
- Cardiovascular disease
- Cataracts
- Celiac disease
- Constipation (< 1 per day)
- Cutaneous Vasculitis
- Chronic Fatigue
- Chronic Hepatitis, primary Biliary Cirrhosis or Bladder Cancer
- Dementia
- Depression
- Dermatitis Herpetiformis
- Dermatomyositis
- Dyslipidemia
- Pre-Diabetes
- Diabetes: Type-1 or Type-2
- Erythema Nodosum
- Epilepsy
- Food Allergies and Intolerances
- Food Cravings
- Gastroesophageal Reflux
- Gastrointestinal Malignant Tumor
- Gluten Encephalopathy
- Gluten Intolerance
- Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
- Head Trauma
- Headaches
- Heartburn
- Hemorrhaging at low blood pressure
- Huntington's disease or degeneration of nerve cells
- Ichthyosiform Dermatoses
- Inflammation
- Iron deficiency
- Irregular Heartbeats (arrhythmias)
- Irritability
- Infantile Spasms
- Irregular Insulin or Insulin Resistance
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Low Blood Pressure (hypotension)
- Lupus
- Metabolic Syndrome (≈ 64 million or 34% of adults in the US)
- Excess Fat around the waist (Men ≥ 100cm-40"; women ≥ 90cm-35")
- High Triglycerides (≥ 150 mg/dL)
- Low HDL-C Cholesterol (Men < 40 mg/dL; women < 50 mg/dL)
- Predominance of small and dense LDL-C Cholesterol particles
- Hypertension (≥ 130/85 mmHg)
- High Fasting Glucose (≥ 100 mg/dL) or Impaired Glucose Tolerance
- Migraines
- Mitochondrial dysfunction
- Muscle Aches or Weakness
- Narcolepsy or Sleep disorder
- Nutritional deficiencie: protein, fatty acids and vitamins B12, D, E, K, folate, iron and zinc
- Overweight
- Obesity
- Oral Ulcers
- Parkinson's disease
- Premature Aging
- Polycystic Ovarian disease
- Premature Aging or Progeroid syndrome
- Psoriasis
- Pyoderma Gangrenosum
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Schizophrenia
- Seizures
- Small Intestinal Lymphoma
- State Pro-Inflammatory or Pro-Coagulant
- Stroke
- Tourette Syndrome
- Ulcerative Colitis
- Vitiligo
* Cancer = "Immune System Overload"
…continue reading and study these material in detail!
We accept that in the last 45 years we have been bombarded by wrong science on nutrition, full of political and economic interests. It is easy to test this hypothesis in a simple way. Looking at the population of developed countries we find that degenerative diseases are in a drastic growth. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 39.8% of U.S. adults are obese. In 2016, 72.7% of males were overweight compared to 63.2% of females. In addition, the Pharmaceutical and Health industry is one of the largest and most powerful in the world—the largest pharmaceutical companies showed a combine income of $845.7 billion dollars in 2019. It is clear that people have a health problem!
Currently the population is in a state of "intellectual pollution", full of false data presented in wonderfully beautiful words without any concrete content. By accepting the need to "empty the glass" the first step materializes, which leads to the encounter of the solution. That is, to realize that, "the knowledge that took us to the problem, will not provide the solution." This paradigm allows the flexibility for new hypotheses and to test their results.

This requires understanding that man is composed of four(4) bodies that make up its Being, and they are an integral part of the solution:
- The Physical body with all biological structures
- The Emotional body with cumulative unresolved resentments hidden in the unconscious
- The Mental body containing our beliefs
- The Spiritual body formed by internal and external energy relationships
This segment of Nutrition focuses on providing resources and tools directed to the first three bodies through Conscious Integrative Nutrition.
Chi Kung focuses on breath and kinesiology alignment, Kundalini Yoga on body energy management, Meditation on energetic communication (interior/exterior), and Shen Kung over long distance energy management.
Fed Up! - Documentary for Kevin
ENZYME BASICS
There are three basic categories of enzymes:
- Digestive
- Metabolic
- Food based
Digestive enzymes, as their name implies, help you break down food into smaller parts that can be absorbed, transported and utilized by every cell in your body. Digestive enzymes are extra-cellular—meaning, they are found outside your cells.
Metabolic enzymes are intra-cellular—meaning, inside your cells, where they help the cell carry out a variety of functions related to its reproduction and replenishment.
Your pancreas produces most of these digestive and metabolic enzymes.
Fortunately, you get (or should be getting) many enzymes from the foods you consume—particularly, raw foods. These directly help with your digestive process.
The more raw foods you eat, the lower the burden on your body to produce the enzymes it needs, not only for digestion, but for practically everything. Whatever enzymes are not used up in digestion are then available to help with other important physiological processes.
[ read the comple article... ]
Enzyme Basiscs 5 Videos
Obesity Will Soon Overtake Smoking as Lead Cause of Cancer
By Dr. Mercola July 27, 2015
For decades, smoking was one of the leading causes of cancer, but that's about to change.
Obesity will likely claim the lead spot as the principal cause of 10 different types of cancer within the next decade, according to cancer specialists who discussed the trend at this year's American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) conference in Chicago.
"They said spiraling rates of obesity meant that cancer—once seen as a disease of old age—was now increasingly being diagnosed up to two decades earlier than in the past. Their figures suggest one in five cancer deaths in Britain is caused by excess weight," The Telegraph reports.
The links between obesity and cancer are quite clear, and excess weight can increase your risk of cancer rather significantly. For example, obese women increase their risk of womb cancer by 600 percent.
Your risk for breast, prostate, colon, and all the other gynecological cancers is also elevated, primarily due to the hormone imbalances associated with obesity, which tend to fuel tumor growth.
Low-Fat Foods Are Making You Fatter
Researchers have also found a correlation between obesity and increased risk for cancer relapse. Overweight survivors of prostate cancer treatment were found to have a three percent higher rate of relapse compared to their slimmer counterparts. They also had seven percent higher odds of the cancer spreading.
Obesity: Weight Modulation
The question is, How many excess pounds do we have?
Research has unequivocally established that the relevant energy balance isn't between the calories we consume and the calories we expend (law of thermodynamics), but between the calories—in the form of free fatty acids, glucose, and glycerol—passing in and out of the fat cells. If more and more fatty acids are fixed in the fat tissue than are released from it, obesity will result. And while this is happening, the energy available to the cells is reduced by the "relative unavailability of fatty acids for fuel." The consequence will be what Edwin Astwood called internal starvation." And as this research had now made clear, the critical molecules determining the balance of storage and mobilization of fatty acids, of lipogenesis and lipolysis, are glucose and insulin—i.e., carbohydrates and the insulin response to those carbohydrates.

The amount of glycerol phosphate available to the fat cells to accumulate fat—to bind the fatty acids together into triglycerides and lock them into the adipose tissue—also depends directly on the carbohydrates in the diet. Dietary glucose is the primary source of glycerol phosphate.
The more carbohydrates consumed, the more glycerol phosphate available, and so the more fat can accumulate. For this reason alone, it may be impossible to store excess body fat without at least some carbohydrates in the diet and without the ongoing metabolism of these dietary carbohydrates to provide glucose and the necessary glycerol phosphate.
Thus, the storage of fat, and therefore the production and maintenance of obesity, cannot take place unless glucose is being metabolized. Since glucose cannot be used by most tissues without the presence of insulin, it also may be stated categorically that obesity is impossible in the absence of adequate tissue concentrations of insulin.
Thus an abundant supply of carbohydrate food exerts a powerful influence in directing the stream of glucose metabolism into lipogenesis, whereas a relatively low carbohydrate intake tends to minimize the storage of fat."
Insulin works to deposit calories as fat and to inhibit the use of that fat for fuel. Dietary carbohydrates are required to allow this fat storage to occur. Since glucose is the primary stimulator of insulin secretion, the more carbohydrates consumed—or the more refined the carbohydrates—the greater the insulin secretion, and thus the greater the accumulation of fat.
"Carbohydrates are driving insulin which is driving fat."
The Mathematics of Weight Loss
How Fat Gets Burned 4 Videos
The Secrets of Sugar
Gastric Surgeries
CARBOHYDRATE "GLUCOSE" METABOLISM
Most carbohydrates provide about 4 kcal/gr in their pure dry form. However, most prepared carbohydrate foods (fresh bread, cooked rice/pasta/potato, juices) contain more water than carbohydrate, which "dilutes" out the calorie count somewhat. Thus 100 grams of mashed potatoes contains only 100 kcal or so (before you add the butter or gravy!). Granulated sugar, on the other hand, is pure dry carbohydrate, so the 4 grams in a level teaspoon provides 16 kcal. Once eaten, most carbohydrates are digested and turned into glucose, which is also what we commonly call blood sugar. The one major exception to this rule is fructose, which metabolically cannot be made directly into glucose.
At any point in time in a healthy non-diabetic individual, there is a little over one(1) "teaspoon" of free glucose in the body, 10grs circulating in the bloodstream and another 10grs diffused into extra-cellular fluid. This means that when you digest and absorb a cup of mashed potatoes or rice, most of the 200 kcal of glucose entering the bloodstream when it gets digested has to be rapidly cleared to someplace else to keep blood sugar in the normal range. If it weren't, blood sugar would rise to more than twice normal within 2 hrs after a meal, and you'd have an instant case of diabetes. Both types of diabetes are diseases caused by the body's inability to dispose of glucose entering the bloodstream. It comes in two general varieties—Type-1 if your body can't make insulin, and Type-2 if you can make insulin but your cells tend to ignore the insulin signal (aka insulin resistance).
So where does glucose go when it leaves the bloodstream? Normally much of it gets taken up into muscle and burned immediately or stored as little starchlike granules (glycogen) in the cells for later use. Your liver also stores some glucose as glycogen, which it then releases to keep blood sugar normal overnight or during prolonged exercise. And some ingested glucose is used "realtime" by your brain to keep the lights on. But an adult at rest burns at most 50 kcal of glucose per hour, so at least half of that cup of mashed potatoes has to be promptly tucked away in storage, preferably as glycogen.
If you have insulin resistance, your rate of glycogen synthesis in response to eating carbohydrates is considerably impaired. Even if you're adept at storing carbs, there's only so much glycogen that your muscles and liver can store—somewhere between 1000 and 2000 kcal in an adult, depending on how big your muscles are and your training status (exercise training can increase the amount of stored glycogen).
So what happens when you eat more carbs than you can burn right away and your glycogen reserves are already full? Rather than let your blood sugar skyrocket up to diabetic levels, your liver, and to some degree your fat cells, go to work turning that extra glucose into fat—a process called lipogenesis. Once that glucose (or fructose) is made into fat, there is no way back—humans can't make fat back into blood sugar—so lipogenesis is a metabolic one-way street, ending in what for many people becomes a crowded parking lot (your fat cells)
Why Sugar is as Bad as Alcohol (Fructose, The Liver Toxin) 11 Videos
Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic Syndrome describes a collection of metabolic abnormalities. These derangements in combination are an indication of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The common thread linking an ever growing constellation of abnormalities is insulin resistance. Insulin resistance is defined as a diminished response to a given concentration of insulin. While insulin resistance may be doing the dirty work at the cellular level, the ringleader of the metabolic syndrome crime syndicate is dietary carbohydrate. Since the inability to properly metabolize dietary carbohydrate is the direct result when insulin action is impaired, from a functional perspective, insulin resistance can be more accurately described as carbohydrate intolerance.
Obesity is the result of a metabolic disorder since the cells can only accept glucose using insulin produced by the pancreas. Insulin carries glucose from the bloodstream into cells where it is used as fuel. When a cell is healthy it has a large number of insulin receptors. If the cell is exposed to high insulin levels due to an almost permanent presence of glucose—caused by excessive consumption of carbohydrates and refined sugars—cells adapt by reducing the amount of insulin receptors on their surface. This causes the cell to desensitize or become insulin resistant.
By having excess blood glucose, the pancreas orders more insulin production, allowing type 2 diabetes to trigger. By definition, a diabetic is someone who has high levels of blood sugar because their body is unable to move glucose into the cells. This vicious circle is one of the leading causes of:
- arthritis
- autoimmune disorders
- blindness
- cerebral exhaustion
- cognitive impairment and problems thinking
- coronary heart disease (CHD)
- creation and retention of fat
- degeneration of the brain and its functioning
- dementia
- depletion of neurotransmitters including: serotonin, epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine and GABA
- formation of Alzheimer's characteristic plaques
- heart disease such as hypertension
- increased inflammation
- inflammatory disorders
- kidney disease
- neurological disorders (such as Alzheimer's)
- premature death
- promotes cell growth
- reduction of vitamin B and magnesium
- stroke
- triggers glycation
- vital brain tissue shrinkage
Metabolic Syndrome Raises Your Risk of Vitamin E Deficiency
August 08, 2016 www.mercola.com
Obese people with metabolic syndrome are at increased risk for vitamin E deficiency, in part because they need more vitamin E to begin with (due to increased oxidative stress), and in part because their condition impairs their body's utilization of vitamin E.
Metabolic syndrome refers to a cluster of symptoms that include excess abdominal fat, high blood pressure, low HDL cholesterol, high blood sugar and elevated triglycerides. As noted by Maret Traber, Ph.D., who is a principal investigator with the Linus Pauling Institute:
"Vitamin E is associated with lipids, or the fats found in the blood, but it's mostly just a micronutrient that's going along for the ride ... [T]issues of obese people are rejecting intake of some of these lipids because they already have enough fat ... In the process they also reject the associated vitamin E."
Taking your vitamin E with some healthy fat, such as coconut oil or avocado can help increase the bioavailability of the vitamin E.
Reference: Science Daily November 2, 2015 [17] Science Daily October 7, 2015
TREATING TYPE-2 DIABETES AS CARBOHYDRATE INTOLERANCE
Excerpt from "The Art and Science of Low Carbohydrate Living" by Phinney, Stephen; Volek, Jeff (2011-07-08)"
The hallmark of type-2 diabetes is insulin resistance, but the actual biology of its underlying cause remains obscure. However, the two best predictors of who will develop diabetes in a cohort of healthy subjects are biomarkers of inflammation (such as C-reactive protein [CRP] and interleukin-6 [IL-6]) and the biomarker of lipogenesis, palmitoleic acid (POA) in the serum cholesteryl ester fraction. So absent a better explanation of the root cause of this disease, it makes sense that it is driven by inflammation and the diversion of dietary carbohydrate into secondary disposal pathways. Furthermore, these two processes are mechanistically linked together by increased Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) production damaging membranes, leading to insulin resistance.
If this is indeed a primary underlying pathophysiology of type-2 diabetes, then it follows that the optimum treatment of type-2 diabetes is reduced dietary carbohydrate intake. After all, very low carbohydrate diets reduce the body's level of inflammation, particularly in conditions such as metabolic syndrome in which it is typically elevated. And restricting carbohydrate intake reduces the total burden of glucose needing disposal, taking the pressure off of secondary disposal pathways like lipogenesis.
On the continuum of insulin resistance, impaired glucose tolerance and more generally metabolic syndrome often progress to overt type-2 diabetes, and therefore the latter represents a more severe form of carbohydrate intolerance. This may mean that in its long-term management, daily carbohydrate intake has to be kept lower in a type-2 diabetic than in someone with less severe insulin resistance. But it also means that a well formulated low carbohydrate diet will tend to produce striking improvements when implemented in type-2 diabetics.
So what evidence is there that this approach actually works? That depends upon who you ask. The American Diabetes Association has been strongly against low carbohydrate diets for decades, but recently altered their position to acknowledge that there may be a role for diets lower in carbohydrate than they have previously been advocating.
And then there is clinical experience and the published literature. Let's start with a clinical case. This case was the first patient that Steve Phinney ever put on a ketogenic diet, occurring during his medical residency under the direction of Dr. Ethan Sims at the University of Vermont. The outcome for this patient was so remarkable that it helped shape Steve Phinney's research career.
Reference: "The Art and Science of Low Carbohydrate Living" by Phinney, Stephen; Volek, Jeff (2011-07-08] See below the video presentation "The Many Facets of Keto-Adaptation: Health, Performance, and Beyond"
Defining Carbohydrate Intolerance
Given this emerging understanding of dietary carbohydrate as both an underlying cause and exacerbator of extant insulin resistance, it is instructive to view insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome and type-2 diabetes as carbohydrate intolerant conditions. What does carbohydrate intolerance mean? In medicine, intolerance is characterized by extreme sensitivity (in a negative way) or allergy to a drug, food, or other substance. Common forms of food intolerances include abnormal responses to lactose and gluten ingestion that in both cases promptly improve when the offending substances are restricted in the diet. In a person intolerant to carbohydrate, there is an exaggerated glucose and insulin response to a given amount of carbohydrate ingested.
A more insidious manifestation of insulin resistance, because of impaired glucose uptake into muscle, is a propensity to divert ingested carbohydrate to the liver where it is converted to fat. Metabolism of carbohydrate through de novo lipogenesis leads to increased plasma triglycerides and dyslipidemia. This is partially driven by a down-regulation of the insulin response and decreased glucose uptake in extrahepatic tissues.
Less well understood is how dietary carbohydrate impacts immune function and inflammatory mechanisms, but another facet of carbohydrate intolerance is likely an aberrant inflammatory response to carbohydrate intake. Clearly the normal response to carbohydrate in insulin sensitive tissues is disturbed in insulin resistance, which subscribes to the definition of intolerance. Put simply, consuming too much carbohydrate is like metabolic kryptonite if you already have insulin resistance.
The Many Facets of Keto-Adaptation: Health, Performance, and Beyond
Wheat in Human Health (Gluten + Glyphosate)
Today's wheat originates from the genetic alterations of Norman E. Borlaug, sponsored by the Rockefeller Foundation. From 1964 to 1979 he directed the International Center for Improvement of Maize and Wheat in Mexico. Since the forties, his work in research programs developed in Mexico laid the foundation of the "green revolution" and the variety selected by Borlaug showed a great adaptation to almost any type of climate, altitude and time of planting. Borlaug's wheat spread throughout the world and showed unprecedented performance. He developed varieties of high-yielding wheat resistant to disease in Mexico and introduced varieties adapted to India and Pakistan in the fifties and sixties, for which he received the Nobel Peace Prize in 1970.
Among the most common and consumed are the:
- Common wheat most widely cultivated in the world (Triticum aestivum)
- Wheat for making macaroni, spaghetti and other pastas and couscous semolina (Triticum durum)
- Wheat for cookies (Triticum compactum)
These wheat contain a protein called gliadin acting as an opiate in the brain, which stimulates appetite, to the point that makes us consume an average of 440 additional calories per day, blocking the leptin hormone (our natural satiation mechanism). It also contains amylopectin A which is a super-carbohydrate that is converted to glucose in the blood more easily.
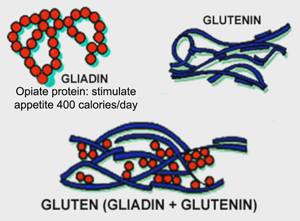
Gliadins are known for their role, along with glutenin, in the formation of gluten. These proteins are essential to allow the bread to rise during preparation and gives it its shape during cooking. They are associated with one of the most important nutritional diseases such as celiac disease, accelerates obesity, aging, renal dysfunction, dementia, atherosclerosis and arthritis. It also produces advanced glycation affecting collagen and elastin which are caramelized.
Dr. Alessio Fasano, from Harvard University, found a direct link between the consumption of gluten and increased intestinal permeability and generalized inflammation throughout the body. The dangers of intestinal permeability are even more serious than we thought, as recent findings suggest that the inflammation caused by the loss of intestinal integrity may result in blood brain barrier permeability.
Gluten enhances the lipopolysaccharide(LPS) which is a combination of lipids (fat) and sugars, being a major component of the outer membrane of certain Gram negative bacteria which are abundant in the gut and can represent up to 70% of intestinal flora. LPS induces aggressive inflammatory response as it finds its way into the bloodstream. Certain diseases such as Alzheimer's, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel diseases, diabetes, Parkinson, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, depression and even autism are linked to the LPS endotoxin. LPS levels in the blood indicate inflammation not only in general, but also intestinal permeability.
These findings have led some experts to question whether one of the main instigators of disease is not in the brain or spine, but in the intestine. In other words, it is possible that scientists have been looking for the answer in the wrong place all these years.
Wheat consumption has been linked to psychiatric conditions like schizophrenia for over 60 years, but recent research indicates the mind-altering properties of this popular food are, in part, caused by it cutting off blood flow to the frontal cortex of the brain. [ 'Gluten Brain': Wheat Cuts Off Blood Flow To Frontal Cortex. ~ Sayer Ji ]
Glyphosate
Initially introduced in a 1962 patent as an antibiotic, and commercialized in the herbicide Roundup® in 1976, Glyphosate is widely used in both industrial agriculture and residential settings.
Glyphosate is a glycine amino acid that is chemically modified with a phosphate group resulting in its categorization as an organophosphate. It functions as a competitive inhibitor of 5-Enolpyruvylshikimate-3-Phosphate (EPSP) synthase, an enzyme produced by plants and microorganisms that is necessary for the production of the Aromatic Amino Acids which are necessary constituents of critical plant and human protein structures including hormones and cell membrane components. [Disorders of Aromatic Amino Acid Metabolism]
Aromatic Amino Acids inhibited by Glyphosate may include:
- Phenylalanine
- Tyrosine
- Tryptophan
- Histidine
- Throxine
- L-DOPA
- 5-Hydroxytryptophan
With these amino acids inhibited, protein synthesis is arrested, leading to retarded plant growth and eventually death. Glyphosate's high solubility in water and ability to be absorbed by plants is another reason for its herbicidal efficacy, and its rapid penetration into the ecosystem.
Hundreds of millions of pounds of glyphosate are applied on U.S. farms, and more than 1.2 billion pounds are used worldwide each year. The volume of usage of this herbicide has led to reports of significant levels of glyphosate in water, air, rainfall and even human breast milk.
For decades, the environment―rivers, lakes, fields, humans, livestock and wildlife―has been exposed to the toxic effects of glyphosate, the active ingredient in the weed killer Roundup®. The chemical, classified as a probable carcinogen by the World Health Organization in 2015, has been linked to kidney disease, liver damage, birth defects, cancers, Parkinson's disease, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and more.
One of glyphosate's less well-known properties is that it is also an antibiotic, and has been registered as such by the Monsanto.
The combination of Gluten plus Glyphosate in your food can make you lose 80% of the protective membrane barrier system in the gut and brain. The US started doing these combination (Gluten, gliadin + Glyphosate) in 1992 when contaminated the wheat directly―Crop desiccation―or indirectly―75% of the rainfall has Glyphosate and 75% of the air is contaminated with Glyphosate in the US.
Glyphosate removes the medicine from the food by disturbing the " Shikimate pathway" and the " Planta Plastid" in the soil Bacteria, Fungi and Plants that make the Alkaloids, the medicine within our food: [Role of Plant Derived Alkaloids and Their Mechanism in Neurodegenerative Disorders]
- anti-parasite (e.g. quinine)
- antiasthma (e.g. ephedrine)
- anticancer (e.g. homoharringtonine)
- cholinomimetic (e.g. galantamine)
- vasodilatory (e.g. vincamine)
- antiarrhythmic (e.g. quinidine)
- analgesic (e.g. morphine)
- antihyperglycemic activities (e.g. piperine)
In a study, glyphosate, rapidly disrupted the intestinal tight junction barrier in both small intestine and colon epithelial membranes. While the exact mechanism for tight junction dysregulation from glyphosate is unknown, it is plausible that it is similar to how gluten disrupts tight junctions through the upregulation of zonulin and the Zonulin Occludins Toxin (ZOT) pathway. Glyphosate's systemic actions are likely unique due to its small size (molar mass of 169 g/mol) and ability to pass through the plasma membrane, in comparison to gliadin's relatively large size (>30,000 g/mol).
A proposed mechanism by which glyphosate has been shown to decrease Transepithelial Electrical Resistance (TEER) in IEC-6 and Caco-2 cells is by dysregulation of tight junctions. Vasiluk et al. have reported glyphosate mediated disruption of intracellular F-actin fibers resulting in disarrangement of the normal cytoplasmic honeycomb, with nuclei neatly in the middle of the cell, to a more chaotic localization of the nuclei after exposure to the herbicide. We demonstrate this phenomenon again with our IEC-6 data, demonstrating chaotic nuclei distribution following glyphosate exposure.
Reference: Protective Effects of Lignite Extract Supplement on Intestinal Barrier Function in Glyphosate-Mediated Tight Junction Injury, by John J Gildea, David A Roberts and Zachary Bush Dr. Zach Bush MD, Nourish Vermont 2018 Zach Bush, MD Our Role in Today's Disease Epidemics
Inner World, Outer World

DICAMBA
THE HERBICIDE MONSANTO IS PROMOTING TO REPLACE ROUNDUP'S GLYPHOSATE
October 30, 2017 by Michael Edwards
Last updated on: October 30, 2017
Original Article

Dicamba is the active ingredient, or is one of a few active ingredients, in herbicidal products the same way glyphosate is the active ingredient in Roundup®. It's been commonly used for over 70 years in professional landscaping as well as home gardening, and its recent popularity is on the rise thanks to the public gaining knowledge regarding the harmful effects of Monsanto's Roundup®. Monsanto has reintroduced Dicamba as the herbicide for the "next-generation."
The product is causing damage when it drifts onto other fields, and many state agriculture authorities have either banned the substance or are considering such bans. Dicamba lawsuits from commercial farmers are becoming more frequent as well.
Recommended: White Pigment In Processed Food Worsens Inflammatory Bowel
What is Dicamba?
First developed in England during the Second World War, Dicamba is a broad-spectrum herbicide found in several brands of commercial weed killer, including Ortho Weed B Gon, Ace Lawn Weed Killer and Roundup® Max.
Chemically, it's part of a group known as the chlorophenoxy family. More specifically, it is an organochloride, a carbon-based compound, the molecules of which contain atoms of the element chlorine. It is derived from benzoic acid, a substance occurring naturally in several plant species and commonly used as a food preservative.
Related: Dicamba Drift Lawsuit Lawyer – Crop Damage Compensation
Recommended: Too Much Sugar Can Lead to a Higher Risk of Cancer – Study Confirms
For a toxin, Dicamba may be safer to humans than glyphosate. It seems we pass it through our urine, and studies indicate that residues do not bioaccumulate in biological systems. To say a product is "safer," compared to glyphosate, certainly does not indicate that the product is safe, and no long term studies have been done on the health effects of Dicamba. It's clearly not good for the environment, and it doesn't belong in our food supply.
Almost exactly a year ago, on Oct. 27, 2016, farm worker Allan Curtis Jones allegedly shot and killed soybean farmer Mike Wallace on a county road in Arkansas. The sheriff later told reporters that the two men had been arguing. Their dispute, the sheriff said, apparently revolved around a phenomenon known in the region as 'Dicamba drift' – NBC News
Related: PCBs, Roundup, and Dicamba – Monsanto's Current Problems
In the heartland states, NBC reports that farmers are pitted against each other. Farmers not using the product report the chemical has wafted onto their fields and damaged their crops which are not genetically modified to withstand Dicamba.
Jones has pleaded not guilty to a first-degree murder charge. He is slated to go to trial in December.
According to the state's farm bureau website, Arkansas ranks third in domestic cotton production, accounting for approximately 7% of the national crop. The state comes in at 10 in soybean production, and about half of that is exported.
Must Read:
Understanding and Detoxifying Genetically Modified Foods
MIT Researcher Reveals the Correlation Between Monsanto's Roundup® and Autism
Sources:
Dicamba Drift: Monsanto Defends Herbicide as Farmers Say It Harms Crops – NBC News
Ag Facts – Arkansas Farm Bureau
Chemical Watch Factsheet – Beyond Pesticides
The Dicamba Drift Crop Damage Lawsuit – Levin law
Exposure Risks
Dicamba can cause severe, permanent damage to the eyes. People exposed in this way should thoroughly flush their eyes with running water for 15 minutes.
The Extension Toxicology Network lists Dicamba as moderately toxic if ingested and slightly toxic if inhaled or applied to skin. Most people who suffer poisoning through ingesting or breathing the herbicide recover in two to three days with no permanent effects.
Symptoms of Dicamba Poisoning:
- Loss of appetite
- Vomiting
- Muscle weakness
- Slowed heart rate
- Shortness of breath
- Excited or depressed behavior
- Benzoic acid in urine
- Incontinence
- Bluing of gums and skin
- Repeated muscle spasms leading to exhaustion
- Irritation of linings in the nasal passages and lungs
- Loss of voice
The National Pesticide Information Center reports that there are no data that show children have increased sensitivity specifically to Dicamba. But children generally are more sensitive to herbicide exposure.
Birds are not likely to suffer harm from eating salt forms of the herbicide but acid versions can be moderately toxic to them. Several studies have found Dicamba is relatively non-toxic to fish.
Exposure Risks
If sprayed on soil, the herbicide will be half gone in 30 to 60 days. Microbes and water in soil will also speed up its breakdown. Microbes and sunlight can break down Dicamba in water.
Source: National Pesticide Information Center
Animal studies have found no serious side effects from long-term exposure. Some rats that had been fed Dicamba for 90 days did not gain as much weight as rats that had not been fed the herbicide. And rabbits that had the chemical on their skin for 21 days experienced skin irritation but their internal organs were not affected. Animal studies do not necessarily mean human exposure would have the same results.
Please seek the advice of a qualified professional before making decisions about your health or finances.
Sources: ConsumerNotice.org
Is Gluten Free Healthy? The REAL Truth About Grains
The Hacking of the American Mind
How Corporations Ruined Food
Dr. Joseph Mercola in his book "Fat for fuel: A revolutionary Diet to Combat Cancer, Boost Brain Power, and Increase Your Energy" explains a couple of ways in which Glyphosate damages the mitochondria:
Glyphosate―the main active ingredient in the toxic herbicide Roundup®―is an enormous threat to your mitochondrial health. Because many vegetable oils, and the processed foods that contain them, are made out of genetically modified corn, soybeans, and canola, they are highly likely to be contaminated with this ubiquitous chemical. This is dire news, given that nearly 2 million tons of glyphosate have been dumped into American soil from 1974 to 2016. Worldwide, nearly 10 million tons have been applied in that same time frame.
There are two main ways glyphosate damages your mitochondria:
- The first involves manganese, a mineral that our bodies need in small amounts for healthy bones, immune function, and neutralization of free radicals. Glyphosate binds manganese and many other important minerals in plants sprayed with Roundup®, with the result that a creature that eats the plants will not get the benefit of these minerals. Glyphosate can also bind to and deplete these minerals from your body. This is a problem because your mitochondria require manganese to convert superoxide, a potentially harmful by-product of oxygen metabolism, into water. This is a critical process that protects your mitochondria from oxidative damage. Without manganese, this mechanism is severely compromised.
- Glyphosate also interferes with Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production by affecting your mitochondrial membranes. When coupled with the so-called "inert solvents" included in Roundup®, the toxicity of glyphosate is magnified as much as 2,000-fold. This makes the membrane more permeable, allowing the glyphosate to go straight to the heart of the mitochondria.
[The red highlights are mine]
ARTICLES
|
Uncovered: Monsanto campaign to get Séralini study retracted |
Key evidence withheld as 'trade secret' in EU's controversial risk assessment of glyphosate |
How Gluten Destroys Thyroid Health
It's a case of mistaken identity. The molecular structure of gliadin, the protein portion of gluten, closely resembles that of the thyroid gland. When gliadin breaches the protective barrier of the gut, and enters the bloodstream, the immune system tags it for destruction. These antibodies to gliadin also cause the body to attack thyroid tissue. This means if you have autoimmune thyroid disease (AITD) and you eat foods containing gluten, your immune system will attack your thyroid.
Even worse, the immune response to gluten can last up to 6 months each time you eat it. This explains why it is critical to eliminate gluten completely from your diet if you have AITD. There's no "80/20" rule when it comes to gluten. Being "mostly" gluten-free isn't going to cut it. If you're gluten intolerant, you have to be 100% gluten-free to prevent immune destruction of your thyroid.
Read the complete article:
[ The Most Important Thing You May Not Know About Hypothyroidism ]
[ The Gluten-Thyroid Connection ]
White flour contains diabetes-causing contaminant Alloxan
You may want to think twice before eating your next sandwich on white bread. Studies show that alloxan, the chemical that makes white flour look "clean" and "beautiful," destroys the beta cells of the pancreas. That's right; you may be devastating your pancreas and putting yourself at risk for diabetes, all for the sake of eating "beautiful" flour. Is it worth it?
Scientists have known of the alloxan-diabetes connection for years; in fact, researchers who are studying diabetes commonly use the chemical to induce the disorder in lab animals. In the research sense, giving alloxan to an animal is similar to injecting that animal with a deadly virus, as both alloxan and the virus are being used specifically to cause illness. Every day, consumers ingest foods made with alloxan-contaminated flour. Would they just as willingly consume foods tainted with a deadly virus? Unless they had a death wish, they probably would not. Unfortunately, most consumers are unaware of alloxan and its potentially fatal link to diabetes because these facts are not well publicized by the food industry.
How does alloxan cause diabetes? According to Dr. Hari Sharma's Freedom from Disease, the uric acid derivative initiates free radical damage to DNA in the beta cells of the pancreas, causing the cells to malfunction and die. When these beta cells fail to operate normally, they no longer produce enough insulin, or in other words, they cause one variety of adult-onset type 2 diabetes. Alloxan's harmful effects on the pancreas are so severe that the Textbook of Natural Medicine calls the chemical "a potent beta-cell toxin." However, even though the toxic effect of alloxan is common scientific knowledge in the research community, the FDA still allows companies to use it when processing foods we ingest.
[ Read the full article from Natural News ]
[ The Little-Known Secrets about Bleached Flour ]
The mechanisms of Alloxan and streptozotocin-induced diabetes
Alloxan and streptozotocin are toxic glucose analogues that preferentially accumulate in pancreatic beta cells via the GLUT2 glucose transporter. In the presence of intracellular thiols, especially glutathione, alloxan generates reactive oxygen species (ROS) in a cyclic redox reaction with its reduction product, dialuric acid. Autoxidation of dialuric acid generates superoxide radicals, hydrogen peroxide and, in a final iron-catalysed reaction step, hydroxyl radicals. These hydroxyl radicals are ultimately responsible for the death of the beta cells, which have a particularly low antioxidative defence capacity, and the ensuing state of insulin-dependent ' alloxan diabetes'.
As a thiol reagent, alloxan also selectively inhibits glucose-induced insulin secretion through its ability to inhibit the beta cell glucose sensor glucokinase. Following its uptake into the beta cells, streptozotocin is split into its glucose and methylnitrosourea moiety. Owing to its alkylating properties, the latter modifies biological macromolecules, fragments DNA and destroys the beta cells, causing a state of insulin-dependent diabetes. The targeting of mitochondrial DNA, thereby impairing the signaling function of beta cell mitochondrial metabolism, also explains how streptozotocin is able to inhibit glucose-induced insulin secretion.
[ Read full study from Diabetologia ]
What indeed is going on with wheat?
The good news is that the reason wheat has become so toxic in the United States is not because it is secretly GMO.
The bad news is that the problem lies with the manner in which wheat is harvested by conventional wheat farmers.
You're going to want to sit down for this one. I've had some folks burst into tears in horror when I passed along this information before.
Wheat harvest protocol in the United States is to drench the wheat fields with Roundup® several days before the combine harvesters work through the fields as withered, dead wheat plants are less taxing on the farm equipment and allows for an earlier, easier and bigger harvest.
Pre-harvest application of the herbicide Roundup® or other herbicides containing the deadly active ingredient glyphosate to wheat and barley as a desiccant was suggested as early as 1980. It has since become routine over the past 15 years and is used as a drying agent 7-10 days before harvest within the conventional farming community.
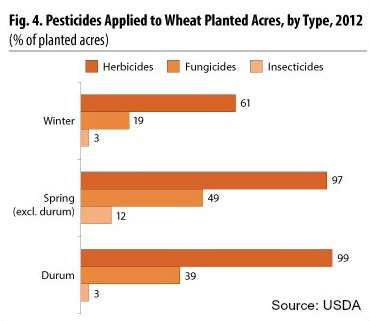
According to Dr. Stephanie Seneff of MIT who has studied the issue in depth and who I recently saw present on the subject at a nutritional Conference in Indianapolis, desiccating non-organic wheat crops with glyphosate just before harvest came into vogue late in the 1990's with the result that most of the non-organic wheat in the United States is now contaminated with it. Seneff explains that when you expose wheat to a toxic chemical like glyphosate, it actually releases more seeds resulting in a slightly greater yield: "It 'goes to seed' as it dies. At its last gasp, it releases the seed" says Dr. Seneff.
According to the US Department of Agriculture, as of 2012, 99% of durum wheat, 97% of spring wheat, and 61% of winter wheat has been treated with herbicides. This is an increase from 88% for durum wheat, 91% for spring wheat and 47% for winter wheat since 1998.
Here's what wheat farmer Keith Lewis has to say about the practice:
I have been a wheat farmer for 50 years and one wheat production practice that is very common is applying the herbicide Roundup® (glyphosate) just prior to harvest. Roundup® is licensed for pre-harvest weed control. Bayer/Monsanto, the manufacturer of Roundup® claims that application to plants at over 30% kernel moisture result in Roundup® uptake by the plant into the kernels. Farmers like this practice because Roundup® kills the wheat plant allowing an earlier harvest.
A wheat field often ripens unevenly, thus applying Roundup® pre-harvest evens up the greener parts of the field with the more mature. The result is on the less mature areas Roundup® is translocated into the kernels and eventually harvested as such.
This practice is not licensed. Farmers mistakenly call it "dessication." Consumers eating products made from wheat flour are undoubtedly consuming minute amounts of Roundup®. An interesting aside, malt barley which is made into beer is not acceptable in the marketplace if it has been sprayed with pre-harvest Roundup®. Lentils and peas are not accepted in the market place if it was sprayed with pre-harvest Roundup®, but wheat is ok. This farming practice greatly concerns me and it should further concern consumers of wheat products.
This practice is not just widespread in the United States either. The Food Standards Agency in the United Kingdom reports that use of Roundup® as a wheat desiccant results in glyphosate residues regularly showing up in bread samples. Other European countries are waking up to the danger, however. In the Netherlands, use of Roundup® is completely banned with France likely soon to follow.
Using Roundup® as a dessicant on the wheat fields prior to harvest may save the farmer money and increase profits, but it is devastating to the health of the consumer who ultimately consumes those ground up wheat kernels which have absorbed a significant amount of Roundup®!
The negative impact of glyphosate exposure is slow and insidious over months and years as inflammation gradually gains a foothold in the cellular systems of the body.
The consequences of this systemic inflammation are most of the diseases and conditions associated with the Western lifestyle:
|
|
And the list goes on and on and on.
"Is the wheat in my 'daily bread' killing me slowly?"
"In my country, where is the wheat for my 'daily bread' coming from?"
[ Read full study from Real Farmacy ]
How Glyphosate interacts with the Gut Bacteria?
While Bayer/Monsanto insists that Roundup® is safe and "minimally toxic" to humans, Samsel and Seneff's research tells a different story altogether. Their report, published in the journal Entropy, argues that glyphosate residues, found in most commonly consumed foods in the Western diet courtesy of sugar, corn, soy and wheat, "enhance the damaging effects of other food-borne chemical residues and toxins in the environment to disrupt normal body functions and induce disease." According to the authors:
"Negative impact on the body is insidious and manifests slowly over time as inflammation damages cellular systems throughout the body."
The main finding of the report is that glyphosate inhibits cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes, a large and diverse group of enzymes that catalyze the oxidation of organic substances. This, the authors state, is "an overlooked component of its toxicity to mammals."
One of the functions of CYP enzymes is to detoxify xenobiotics—chemical compounds found in a living organism that are not normally produced or consumed by the organism in question. By limiting the ability of these enzymes to detoxify foreign chemical compounds, glyphosate enhances the damaging effects of those chemicals and environmental toxins you may be exposed to.
Dr. Stephanie Seneff has been conducting research at MIT for over three decades. She also has an undergraduate degree in biology from MIT and a minor in food and nutrition, and I have previously interviewed her about her groundbreaking insights into the critical importance of sulfur in human health. Not surprisingly, this latest research also touches on sulfur, and how it is affected by glyphosate from food.
"Here, we show how interference with CYP enzymes acts synergistically with disruption of the biosynthesis of aromatic amino acids by gut bacteria, as well as impairment in serum sulfate transport," the authors write.
"Consequences are most of the diseases and conditions associated with a Western diet, which include gastrointestinal disorders, obesity, diabetes, heart disease, depression, autism, infertility, cancer and Alzheimer's disease.
We explain the documented effects of glyphosate and its ability to induce disease, and we show that glyphosate is the 'textbook example' of exogenous semiotic entropy: the disruption of homeostasis by environmental toxins."
[ Read full study from Mercola.com ]
Other recommended related articles:
[ Cholesterol Sulfate and Glyphosate: A Special Interview with Dr. Stephanie Seneff ]
[ Shikimate pathway, microbiome and disease: Health effects of GMOS on humans ]
Glyphosate in your Food The 2 Most DANGEROUS Foods
Understanding Insulin Resistance
By Dr. Eric Berg, DC
Your pancreas is located in the left lower quadrant right by your rib cage and it makes a hormone called insulin.
Insulin responds to sugar (glucose)―it is triggered by anything that has sugar or turns into sugar like bread. Insulin removes sugar from your blood. Normally in your blood you need only about a 100 milligrams of sugar per deciliter. Anything higher or lower than 100 is bad.
- When it goes higher than 100 you get diabetes
- When it goes lower than 100 you will get hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is when you skipping meals and eating way too much sugar which triggers high insulin in your blood making sugar to drop.
Over time your body doesn't like this and it will turn off the insulin receptor and ignore the insulin response―this is called a blocked receptor and this is Insulin Resistance. It forces insulin to go higher and the pancreas to make more insulin to create the same affect. Without insulin your blood sugar will stay high and wear out the pancreas. Sugar is toxic to your body.
Diabetes is really a situation where you have high sugar and it won't come down to 100, passed that point it becomes hypoglycemia turning into type II diabetes. Then there is insulin resistance because you have been eating too much sugar.
Your body protects you from the toxic sugar and several things happen as a consequence, like you will be hungry because insulin has other purposes. The insulin lowers the sugar in the blood, helps you absorb the nutrition in your cells like fatty acids, proteins and vitamins. Without insulin you can't get the nutrition in your cells and you're going to be hungry all the time because you eat but you don't absorb the nutrients. So, you will have a fat person that is starving to death and craving carbohydrates. If you are craving carbs or sweets it is impossible to burn fat.
That's why, overtime, diabetes patients have other health problems―they may go blind, have a destroyed nerve in the feet and the hands and it goes downhill health wise.
This condition will prevent the storage of glycogen in your liver and your muscles which we live off while sleep. If you can't store the sugar as much anymore, you will end up having problems with storing more fat. If we are not storing sugar you will end up storing fat and you will get bigger and bigger. In between meals, because you can't store sugar, you're going to have too many highs and lows. It's the storage of sugar that maintains a nice level.
In your entire body you only need 1 teaspoon (5 grams) of sugar―not directly from sugar but from the foods that you eat.
Even protein and fat can convert into sugar. An 8 oz. typical can of soda or orange juice is about 39 teaspoons of sugar―that is a tremendous stress on the pancreas.
The pancreas has two parts―produces the hormone insulin and enzymes, amylase which helps to digest sugars, pancreatic proteases (such as trypsin and chymotrypsin) which help to digest proteins; and pancreatic lipase which helps to digest fat.
If you continue eating high quantities of sugar, you're going to have all sorts of digestion problems such as:
- inflammation of the pancreas
- pain in your back
- can't digest protein
- bowel problems
- gas
- bloating
- and more
The body is attempting to protect itself from too much insulin by blocking receptors and create resistance and the sugar is going to go high. The body is going to protect the cell from too much insulin and not the blood―that's why the blood starts filling up with sugar.
Triglycerides are blood fats because the cell can't absorb nutrition, protein or fat, it's going to dump them in the blood as blood fats and cholesterol. In type I diabetes the pancreas is asleep―it's the worst you can get because then you will have to be injected with insulin.
Also, "statin medication", recommended to lower cholesterol, increases the risk for diabetes 40% in males and may be as high as 72% in females.
What can be Done?
You will need to lower insulin by doing these things:
- If you are craving sugars, you should be consuming zero "sugars".
- Increase potassium because it will help lower insulin and help you store sugar.
You will want to get potassium from food such as cruciferous, about 7 to 10 cups of vegetables per day or you can take the kale shake.
Eating vegetables will help lower cravings.
- Increase vitamin B1 not from a pill but from nutritional yeast which will greatly assist with lowering insulin. When you consume a bunch of sugar you're a dumping B1 and other nutrition out of your body in your urine.
- Consume protein because it is a nutrient especially for breakfast, if you don't your blood sugars will be off by the end of the day.
Understanding Insulin Resistance 16 Videos
Alternative to Glucose Metabolism
The alternative to glucose metabolism is one of the best hypotheses available for the control of obesity and Weight modulation. It is practical and viable producing concrete results. The following are some of the documented health benefits:
- Acts as an antidepressant
- Calms inflammation in the brain and throughout the body
- Decrease mitochondrial oxidative stress
- Enhances heart function by improving efficiency and strength while utilizing less oxygen. Increase the hydraulic efficiency of the heart by 25% in comparison to glucose
- Enhances anti-inflammatory pathways
- Enhances DNA repair
- Enhances Glutathione production
- Help stabilize mtDNA
- Increases bioenergetic genes
- Increases Iron absorption
- Increases mitochondrial biogenesis
- Improves sleep apnea
- Improves hypertension and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Improves overall health and increases life span
- Increases antioxidant pathways
- Increases absorption of fat-soluble vitamin K2
- Increases cellular resistance to stress and improves recovery after surgery
- Increases sperm vitality and motility, important for successful fertilization
- Maintains optimum cell membrane composition
- May be helpful in alleviating the detrimental effects of almost every disease state due to the ability to calm inflammation and increase oxygen utilization
- Mitigates symptoms of autism
- Mitigates the effects of insulin resistance by mimicking the acute metabolic effects of insulin
- Optimizes Mitochondria energy production (ATP)
- Prevents migraine headaches
- Promotes Brain ATP in the Hippocampus
- Protects against brain damage caused by cerebral hypoxia and improves survival
- Protects against brain damage caused by stroke
- Protects Parasympathetic activity
- Protects from Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack)
- Protects against cancer, especially brain cancer
- Protects against diabetes. Reduces the liver's output of glucose and increases insulin production, thus improving blood sugar control and carbohydrate tolerance
- Protects against epileptic seizures, including difficult-to-treat drug-resistant seizures
- Protects against infantile spasms and narcolepsy
- Protects against microbial infections
- Protects against neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, Huntington's, and ALS(Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis)
- Protects against polycystic ovary syndrome
- Protects against symptoms of hypoglycemia
- Protects brain cells from chemical toxins
- Protects the brain against damage caused by physical trauma
- Protects the gallbladder from gallstones during major weight loss
- Provides an alternative high-potency energy source that can be used by every organ in the body, except for the liver
- Reduces the formation of destructive free radicals
- Supplies the substrate from which new neurons can be synthesized
- Useful aid for weight management and obesity treatment


[ What are NSAIDs? ] NonSteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
You can train your body to burn fat by changing your diet over a period of a few weeks, thereby turning blood sugar and glycogen into secondary fuels. Once you make this transition, you can then train harder, perform longer, and recover faster.
A diet consisting mostly of healthy higher-quality fat and protein can support remarkable growth, physical well-being and function, promoting the capabilities of the individual over commonly assumed societal norms.
Low carbohydrate diets are anti-inflammatory, producing less oxidative stress during exercise and more rapid recovery between exercise sessions.
Physiological adaptation to low carbohydrate living allows much greater reliance on body fat, not just at rest but also during exercise, meaning much less dependence on muscle glycogen and less need to reload with carbohydrates during and after exercise.
Low carbohydrate adaptation accelerates the body's use of saturated fats for fuel, allowing a high intake of total fats (including saturates) without risk.
At the practical level, effective training for both endurance and strength/power sports can be done by individuals adapted to carbohydrate restricted diets, with desirable changes in body composition and power-to-weight ratios.
Reference:
www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/obesity-overweight.htm
www.bbc.com/news/business-28212223
Good Calories, Bad Calories, Gary Taubes
Stop Alzheimer's Now!, Bruce Fife, N.D.
The Art and Science of Low Carbohydrate Living, Phinney, Stephen; Volek, Jeff (2011-07-08)
Ketogenic Diet: Connection between Mitochondria and Diet, Gabriela Segura, MD, Consultant Cardiologist, Friday, 9 August 2013
Davis, William (2014-09-17), "Sin trigo, gracias" Penguin Random House Grupo Editorial España
Obesity Warrior
Fat Does Not Make You Fat 5 Videos
How to Get Fat Without Really Trying. The Skinny on Obesity
KETOGENIC DIET: CONNECTION BETWEEN MITOCHONDRIA AND DIET
Gabriela Segura, MD— August 2013
Introduction
Ketosis is an often misunderstood subject. Its presence is thought to be equal to starvation or a warning sign of something going wrong in your metabolism. But nothing could be farther from the truth, except if you are an ill-treated Type-1 diabetic person.[1] Ketones—contrary to popular belief and myth—are a much needed and essential healing energy source in our cells that comes from the normal metabolism of fat.
The entire body uses ketones in a more safe and effective way that the energy source coming from carbohydrates—sugar AKA glucose. Our bodies will produce ketones if we eat a diet devoid of carbs or a low carb diet (less than 60 grams of carbs per day).[2] By eating a very low carb diet or no carbs at all (like a caveman) we become keto-adapted.
In fact, what is known today as the ketogenic diet was the number one treatment for epilepsy until Big Pharma arrived with its dangerous cocktails of anti-epileptic drugs. It took several decades before we heard again about this diet, thanks in part to a parent who demanded it for his 20-month-old boy with severe seizures. The boy's father had to find out about the ketogenic diet in a library as it was never mentioned as an option by his neurologist. After only 4 days on the diet, his seizures stopped and never returned.[3] The Charlie Foundation was born after the kid's name and his successful recovery, but nowadays the ketogenic diet is available to the entire world and it's spreading by word of mouth thanks to its healing effects.
It is not only used as a healthy lifestyle, it is also used for conditions such as infantile spasms, epilepsy, autism, brain tumors, Alzheimer's disease, Lou Gehrig's disease, depression, stroke, head trauma, Parkinson's disease, migraine, sleep disorders, schizophrenia, anxiety, ADHD, irritability, polycystic ovarian disease, irritable bowel syndrome, gastroesophageal reflux, obesity, cardiovascular disease, acne, type 2 diabetes, tremors, respiratory failure and virtually every neurological problem but also cancer, and conditions were tissues need to recover after a loss of oxygen.[4]
Our body organs and tissues work much better when they use ketones as a source of fuel, including the brain, heart and the core of our kidneys. If you ever had a chance to see a heart working in real time, you might have noticed the thick fatty tissue that surrounds it. In fact, heart surgeons get to see this every day. A happy beating heart is one that is surrounded by layers of healthy fat. Both the heart and the brain run at least 25% more efficiently on ketones than on blood sugar.
Ketones are the ideal fuel for our bodies unlike glucose—which is damaging, less stable, more excitatory and in fact shortens your life span. Ketones are non-glycating, which is to say, they don't have a caramelizing aging effect on your body. A healthy ketosis also helps starve cancer cells as they are unable to use ketones for fuel, relying on glucose alone for their growth.[5] The energy producing factories of our cells—the mitochondria—work much better on a ketogenic diet as they are able to increase energy levels on a stable, long-burning, efficient, and steady way. Not only that, a ketogenic diet induces epigenetic changes[6] which increases the energetic output of our mitochondria, reduces the production of damaging free radicals, and favors the production of GABA—a major inhibitory brain chemical. GABA has an essential relaxing influence and its favored production by ketosis also reduces the toxic effects of excitatory pathways in our brains. Furthermore, recent data suggests that ketosis alleviates pain other than having an overall anti-inflammatory effect.[7]
The ketogenic diet acts on multiple levels at once, something that no drug has been able to mimic. This is because mitochondria is specifically designed to use fat for energy. When our mitochondria uses "healthy high-quality fat" as an energetic source, its toxic load is decreased, expression of energy producing genes are increased, its energetic output is increased, and the load of inflammatory energetic-end-products is decreased.
The key of these miraculous healing effects relies in the fact that fat metabolism and its generation of ketone bodies (beta-hydroxybutyrate & acetoacetate) by the liver can only occur within the mitochondrion, leaving chemicals within the cell but outside the mitochondria readily available to stimulate powerful anti-inflammatory antioxidants. The status of our mitochondria is the ultimate key for optimal health and while it is true that some of us might need extra support in the form of nutritional supplementation to heal these much needed energy factories, the diet still remains the ultimate key for a proper balance.
Our modern world's staple energetic source is sugar which needs to be processed first in the cell soup before it can be passed into the energy factory of the cell—the mitochondrion. Energy sources from fat don't require this processing; it goes directly into the mitochondria for energetic uses. That is, it is more complicated to create energy out of sugar than out of fat . As Christian B. Allan, PhD and Wolfgang Lutz, MD said in their book "Life Without Bread":
Carbohydrates are not required to obtain energy. Fat supplies more energy than a comparable amount of carbohydrate, and low-carbohydrate diets tend to make your system of producing energy more efficient. Furthermore, many organs prefer fat for energy.
The fact is you get more energy per molecule of fat than sugar. How many chronic and autoimmune diseases have an energy deficit component? How about chronic fatigue? Fibromyalgia? Rheumatoid Arthritis? Multiple Sclerosis? Cancer? Back to Allan and Lutz:
Mitochondria are the power plants of the cell. Because they produce most of the energy in the body, the amount of energy available is based on how well the mitochondria are working. Whenever you think of energy, think of all those mitochondria churning out ATP to make the entire body function correctly. The amount of mitochondria in each cell varies, but up to 50% of the total cell volume can be mitochondria. When you get tired, don't just assume you need more carbohydrates; instead, think in terms of how you can maximize your mitochondrial energy production.
If you could shrink to a small enough size to get inside the mitochondria, what would you discover? The first thing you'd learn is that the mitochondria are primarily designed to use fat for energy!
In short, let fat be thy medicine and medicine be thy fat!
You will think that with all of this information we would see ketogenic diets recommended right and left by our health care providers, but alas, that is not the case. Mainstream nutritionists recommend carbohydrates—sugar as the main staple of our diets. The problem with this (and there are several of them) is that in the presence of a high carb diet we are unable to produce ketones from the metabolism of fats, thus, depriving ours bodies from much healing ketone production. The fact that we live in a world which uses glucose as a primary fuel means that we eat a very non healing food in more ways than one.
I have been doing the low carb diet for about a week and a half now and I must say, I am really starting to feel amazing! The first few days my head hurt, I felt lethargic, and my legs felt so heavy. But after I got past that, I have so much energy. I don't get tired anymore around 3pm. The best part is, I am not constantly thinking and obsessing about food. I feel a real sense of inner calm. My skin looks better, my hair looks better too. I have been having bacon and eggs for breakfast, a pork chop or other piece of meat for lunch, and usually some pork and sometimes some green beans for dinner. I have also lost some weight! Woo hoo!—Angela, United States. Sott.net forum.
We have been on a ketogenic diet for nearly three million years and it has made us human. It was the lifestyle in which our brains got nurtured and evolved. But not anymore, unless we all make an effort to reclaim this lost wisdom. Nowadays the human brain is not only shrinking, but brain atrophy is the norm as we age and get plagued with diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, senile dementia and so forth.
In the mean time new research is starting to elucidate the key role of our mitochondria in the regulation of the cell-cycle—the vital process by which a single celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. In the complicated and highly choreographed events surrounding cell-cycle progression, mitochondria are not simple bystanders merely producing energy but instead are full-fledged participants.[8] Given the significant amount of energy needed to make all the nutrients required for cell division, it makes sense that some coordination existed. This long ignored and overlooked connection between the mitochondria and the cell-cycle is something that is worthy of considerable more attention as we understand the role of diet in our bodies. We'll have to take a closer look to this subject of ketosis, as it really holds the key to unlock our transformational pathways that will lead us to an outstanding healthy living.
Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Mitochondria are best known as the powerhouses of our cells since they produce the cell's energy. But they also lead the genetic orchestra which regulates how every cell ages, divides, and dies. They help dictate which genes are switched on or off in every single cell of our organism. They also provide the fuel needed to make new brain connections, repair and regenerate our bodies.
Whether we are housewives, sportsmen or labor people, energy is a topic that concerns us all, every day and in every way. Our well being, behavior and ability to perform the tasks in front of us to do is our individual measure of energy. How do we derive energy from foods that we eat?
There are many man-made myths surrounding energy production in the body and which foods supply energy. Mainstream science says that carbohydrates are what mitochondria use as fuel for energy production. This process is called oxidative metabolism because oxygen is consumed in the process. The energy produced by mitochondria is stored in a chemical "battery", a unique molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Energy-packed ATP can then be transported throughout the cell, releasing energy on demand of specific enzymes. In addition to the fuel they produce, mitochondria als o create a by-product related to oxygen called reactive oxygen species (ROS)—free radicals. But what we are not told is that mitochondria were specifically designed to use fat for energy, not carbohydrate.
Source: Christian B. Allan, PhD and Wolfgang Lutz, MD, Life Without Bread.
There are several very complicated steps in making ATP within mitochondria, but a look at 5 major parts of ATP production will be all that you need to know in order to understand how energy is created within our mitochondria and why fats are the key to optimize their function. Don't get focused on specific names, just look at the whole picture:
Step 1—Transportation of Food-Based Fuel Source into the Mitochondria Fuel must first get into the mitochondria where all the action happens. Fuel can come from carbs or it can come from fats. Fatty acids are the chemical name for fat, and medium and large sized fatty acids get into the mitochondria completely intact with the help of L-carnitine. Think of L-carnitine as a subway train that transports fatty acids into the mitochondria. L-carnitine (from the Greek word carnis means meat or flesh) is chiefly found in animal products.
Fuel coming from carbs needs to get broken down first outside the mitochondria and the product of this breakdown (pyruvate) is the one who gets transported inside the mitochondria, or it can be used to produce energy in a very inefficient way outside the mitochondria through anaerobic metabolism which produces ATP when oxygen is not present.
Step 2—Fuel is Converted into Acetyl-CoA (Acetyl coenzyme A) When pyruvate—the product of breaking down carbs—enters the mitochondria, it first must be converted into acetyl-CoA by an enzymatic reaction.
Fatty acids that are already inside the mitochondria are broken down directly into acetyl-CoA in what is called beta-oxidation.
Acetyl-CoA is the starting point of the next step in the production of ATP inside the mitochondria.
Step 3—Oxidation of Acetyl-CoA and the Krebs Cycle The Krebs cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle or citric acid cycle) is the one that oxidizes the acetyl-CoA, removing thus electrons from acetyl-CoA and producing carbon dioxide as a by-product in the presence of oxygen inside the mitochondria.
Step 4—Electrons are Transported through the Respiratory Chain The electrons obtained from acetyl-CoA—which ultimately came from carbs or fats—are shuttled through many molecules as part of the electron transport chain inside the mitochondria. Some molecules are proteins, others are cofactors molecules. One of these cofactors is an important substance found mainly in animal foods and it is called coenzyme Q10. Without it, mitochondrial energy production would be minimal. This is the same coenzyme Q10 that statins drug block producing crippling effects on people's health. Step 4 is also where water is produced when oxygen accepts the electrons.
Step 5—Oxidative phosphorylation As electrons travel down the electron transport chain, they cause electrical fluctuations (or chemical gradients) between the inner and outer membrane in the mitochondria. These chemical gradients are the driving forces that produce ATP in what is called oxidative phosphorylation. Then the ATP is transported outside the mitochondria for the cell to use as energy for any of its thousands of biochemical reactions.
But why is "healthy high-quality Fat" better than Carbs?
If there were no mitochondria, then fat metabolism for energy would be limited and not very efficient. But nature provided us during our evolution with mitochondria that specifically uses fat for energy. Fat is the fueled that animals use to travel great distances, hunt, work, and play since fat gives more packed-energy ATPs than carbs. Biochemically, it makes sense that if we are higher mammals who have mitochondria, then we need to eat fat. Whereas carb metabolism yields 36 ATP molecules from a glucose molecule, a fat metabolism yields 48 ATP molecules from a fatty acid molecule inside the mitochondria. Fat supplies more energy (33% more) for the same amount of food compared to carbs. But not only that, the burning of fat by the mitochondria—beta oxidation—produces ketone bodies that stabilizes overexcitation and oxidative stress in the brain related to all its diseases, it also causes epigenetic changes that produce healthy and energetic mitochondria and decreasing the overproduction of damaging and inflammatory free radicals among many other things!
Mitochondria regulate cellular suicide—apoptosis, so that old and dysfunctional cells which need to die will do so, leaving space for new ones to come into the scene. But when mitochondria function becomes impaired and send signals that tell normal cells to die, things go wrong. For instance, the destruction of brain cells leads to every single neurodegenerative condition known including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and so forth. Mitochondrial dysfunction has wide-ranging implications, as the health of the mitochondria intimately affects every single cell, tissue and organ within your body.
The catalysts for this destruction is usually uncontrolled free radical production which cause oxidative damage to tissues, fat, proteins, DNA; causing them to rust. This damage, called oxidative stress, is at the basis of oxidized cholesterol, stiff arteries (rusty pipes) and brain damage. Oxidative stress is a key player in dementia as well as autism.
We produce our own anti-oxidants to keep a check on free radical production, but these systems are easily overwhelmed by a toxic environment and a high carb diet, in other words, by today's lifestyle and diet.
Mitochondria also have interesting characteristics which differentiate them from all other structural parts of our cells. For instance, they have their own DNA (referred as mtDNA) which is separate from the widely known DNA in the nucleus (referred as n-DNA). Mitochondrial DNA comes for the most part from the mother line, which is why mitochondria is also considered as your feminine life force. This mtDNA is arranged in a ring configuration and it lacks a protective protein surrounding, leaving its genetic code vulnerable to free radical damage. If you don't eat enough animal fats, you can't build a functional mitochondrial membrane which will keep it healthy and prevent them from dying.
If you have any kind of inflammation from anywhere in your body, you damage your mitochondria. The loss of function or death of mitochondria is present in pretty much every disease. Dietary and environmental factors lead to oxidative stress and thus to mitochondrial injury as the final common pathway of diseases or illnesses.
Autism, ADHD, Parkinson's, depression, anxiety, bipolar disease, brain aging are all linked with mitochondrial dysfunction from oxidative stress. Mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to congestive heart failure, type-2 diabetes, autoimmune disorders, aging, cancer, and other diseases.
Whereas the nDNA provides the information your cells need to code for proteins that control metabolism, repair, and structural integrity of your body, it is the mtDNA which directs the production and utilization of your life energy. A cell can still commit suicide (apoptosis) even when it has no nucleus nor nDNA.
Because of their energetic role, the cells of tissues and organs which require more energy to function are richer in mitochondrial numbers. Cells in our brains, muscles, heart, kidney and liver contain thousands of mitochondria, comprising up to 40% of the cell's mass. According to Prof. Enzo Nisoli, a human adult possesses more than ten million billion (1020) mitochondria, making up a full 10% of the total body weight.[9] Each cell contains hundreds of mitochondria and thousands of mtDNA.
Since mtDNA is less protected than nDNA because it has no "protein" coating (histones), it is exquisitely vulnerable to injury by destabilizing molecules such as neurotoxic pesticides, herbicides, excitotoxins, heavy metals and volatile chemicals among others. This tips-off the balance of free radical production to the extreme which then leads to oxidative stress damaging our mitochondria and its DNA. As a result we get over-excitation of cells and inflammation which is at the root of Parkinson's disease and other diseases, but also mood problems and behavior problems.
Enough energy means a happy and healthy life. It also reflects in our brains with focused and sharp thinking. Lack of energy means mood problems, dementia, and slowed mental function among others. Mitochondria are intricately linked to the ability of the prefrontal cortex—our brain's captain—to come fully online. Brain cells are loaded in mitochondria that produce the necessary energy to learn and memorize, and fire neurons harmoniously.
The sirtuin family of genes works by protecting and improving the health and function of your mitochondria.[10] They are positively influenced by a diet that is non-glycating (non-caramelizing aging effect on your body), i.e. a low carb diet as opposed to a high carb diet which induces mitochondrial dysfunction and formation of reactive oxygen species.
Another thing that contributes to mitochondrial dysfunction is latent viral infection such as the ones of the herpes family. Most, if not all of your "junk" DNA has viral-like properties. If a pathogenic virus takes hold of our DNA or RNA, it could lead to disease or cancer.
Herpes simplex virus is a widespread human pathogen and it goes right after our mitochondrial DNA. Herpes simplex virus establishes its latency in sensory neurons, a type of cell that is highly sensitive to the pathological effects of mtDNA damage.[11] A latent viral infection might be driving the brain cell loss in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease.[12] As I speculated in Heart attacks, CFS (Chronic Fatigue Syndrome), herpes virus infection and the vagus nerve, a latent herpes virus infection might drive more diseases than we would like to admit.
Members of the herpes virus family (i.e. cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus which most people have as latent infections!), can go after our mitochondrial DNA, causing neurodegenerative diseases by mitochondrial dysfunction. But a ketogenic diet is the one thing that would help stabilize mtDNA since mitochondria runs the best on fat fuel. As it happens, Alzheimer's disease is the one condition where a ketogenic diet has its most potential healing effect.[4]
The role of mitochondrial dysfunction in our "modern" age maladies is a staggering one. Optimal energetic sources are essential if we are to heal from chronic ailments. It is our mitochondria which lies at the interface between the fuel from foods that come from our environment and our bodies' energy demands. And it is a metabolism based on fat fuel, a ketone metabolism, the one which signals epigenetic changes that maximizes energetic output within our mitochondria and help us heal.
I am incredulous at how my body is responding. I think I am totally carb intolerant. I've struggled with extreme fatigue/exhaustion for so many years, even with improved sleep in a dark room that I can't tell you how wonderful it is to wake up in the morning, get out of bed and not long to crawl back in, going through the day by will mostly. Also chronic long-standing intestinal issues are finally resolving. A couple of people at work have made comments to the effect that I'm a "different woman", calmer, no more hyperness under pressure, stress seems to roll off of my back as well. I've lost a little weight and although I don't weigh myself, my clothes are definitely looser. I've had the round middle for so many years I was resigned to struggling to bend over to pull my shoes on!—Bluefyre, 56 years old, United States. Sott.net forum
Ketosis—Closer Look
The presence of ketones in the blood and urine, a condition known as ketosis, has been regarded s a negative situation, related to starvation. While it is true that ketones are produced during fasting, ketones are also produced in times of plenty, but not plenty of carbohydrates since a carb metabolism suppresses ketosis. In the absence of most carbs in the diet, ketones will form from fat to supply for energy. This is true even if lots of fats and enough protein are eaten, something that is hardly a starvation condition.
As we already saw, a ketogenic diet has been proved useful in a number of diseases, especially neurological ones. Strictly speaking, a ketogenic diet is a high "healthy high-quality fat" diet in which carbohydrates are either completely eliminated or nearly eliminated so that the body has the very bare minimum sources of glucose. That makes fats (fatty acids) a mandatory energetic fuel source for both the brain and other organs and tissues. If ou are carb intake is high, you'll end up storing both the fat and the carbs in your fat tissue thanks to the hormone insulin. A ketogenic diet is not a high protein diet, which as it happens, can also stimulate insulin. It is basically a diet where you rely primarily on animal foods and especially their fats.
I recently had my annual blood work done (cholesterol, etc.) During the review, my doctor said that everything looked great! He then encouraged me to continue on my great 'low fat, high fruit and veggie diet' that I must be following! I just smiled. Next visit I'm going to tell him about my real 'diet'. Lol—Sott.net forum.
Among the by-products of fat burning metabolism are the so called ketone bodies—acetoacetate, β-hydroxybutyrate and acetone—which are produced for the most part by the liver. When our bodies are running primarily on fats, large amounts of acetyl-CoA are produced which exceed the capacity of the Krebs cycle, leading to the making of these three ketone bodies within liver mitochondria. Our levels of ketone bodies in our blood go up and the brain readily uses them for energetic purposes. Ketone bodies cross the blood brain barrier very readily. Their solubility also makes them easily transportable by the blood to other organs and tissues. When ketone bodies are used as energy, they release acetyl-CoA which then goes to the Krebs cycle again to produce energy.
In children who were treated with the ketogenic diet to treat their epilepsy, it was seen that they become seizure-free even long after the diet ended, meaning that not only did the diet proved to be protective, but also it modified the activity of the disease, something that no drug has been able to do.[13] In Alzheimer's disease, as levels of ketone bodies rise, memory improves. People's starved brains finally receive the much needed fats they need! In fact, every single neurological disease is improved on the ketogenic diet.
The benefits of a ketogenic diet can be seen as fast as one week, developing gradually over a period of 3 weeks. There are several changes in gene expression involving metabolism, growth, development, and allostasis among others.
The hippocampus is a region in your brain that is very vulnerable to stress which makes it lose its brain cells. The hippocampus has to do with memory, learning, and emotion. As it happens, a ketogenic diet promotes the codification of genes which creates mitochondria in the hippocampus, making more energy available. A larger mitochondrial load and more energy means more reserve to withstand much more stress.[14]
In some animal models, there is a 50% increase in the total number of mitochondria in the hippocampus, resulting in more brain ATP.[15] Other animal studies show how communication between brain cells in the hippocampus would remain smooth for 60% longer when exposed to a stressful stimulus compared to their counterparts who didn't had a ketogenic diet.[16] This is very important since too much stress can damage the hippocampus and its capacity to retrieve information, making you "absent-minded" or "brain-scattered", as well as affecting the ability of your prefrontal cortex to think and manage behavior.
A ketogenic diet also increases levels of the calming neurotransmitter—GABA—which then serves to calm down the overexcitation which is at the base of major neuro-degenerative diseases, but also anxiety and other mood problems. A ketogenic diet also increases antioxidant pathways that level the excess production of free radicals from a toxic environment. It also enhances anti-inflammatory pathways.
Ketosis also cleans our cells from proteins that act like "debris" and which contribute to aging by disrupting a proper functioning of the cell.[17] It basically does this by what is known as autophagy which preserves the health of cells and tissues by replacing outdated and damaged cellular components with fresh ones. This prevents degenerative diseases, aging, cancer, and protects you against microbial infections. A ketogenic diet not only rejuvenates you, it also makes a person much less susceptible to viruses and bacterial infections.[18] This is very relevant due to the increasing number of weird viral and bacterial infections that seem to be incoming from our upper atmosphere[19] (for more information see New Light on the Black Death: The Viral and Cosmic Connection), or due to high levels of radiation that creates more pathogenic strains (see Detoxify or Die: Natural Radiation Protection Therapies for Coping With the Fallout of the Fukushima Nuclear Meltdown). Either or, we are more vulnerable than ever due to the state of our mitochondria. But we can prepare for the worst with ketosis.
Ketone-enhanced autophagy is very important because autophagy can target viruses and bacteria that grow inside cells which are very problematical.[20] Intracellular viruses and bacteria can lead to severe mitochondrial dysfunction and ketosis remains by far our best chance against them.
Ketone bodies production through intermittent fasting and the ketogenic diet is the most promising treatment for mitochondrial dysfunction.[21] The longevity benefits seen caloric restriction research is due to the fact that our bodies shift to a fat burning metabolism within our mitochondria. With a ketogenic diet, we go into a fat burning metabolism without restricting our caloric intake.
Ketosis deals effectively with all the problems of a diet rich in carbs—the one recommended by mainstream science: anxiety, food cravings, irritability, tremors, and mood problems among others. It is a crime to discourage the consumption of a high "healthy high-quality fat" diet considering that a ketogenic diet shrinks tumors on human and animal models, and enhances our brain's resiliency against stress and toxicity.
In addition to increasing the production of our body's natural valium—GABA—the increased production of acetyl-CoA generated from the ketone bodies also drives the Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle) to increase mitochondrial NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine nucleotide) which our body uses in over 450 vital biochemical reactions—including the cell signaling and assisting of the ongoing DNA repair. Because the ketone body beta-hydroxybutyrate is more energy rich than pyruvate, it produces more ATP. Ketosis also enhances the production of important anti-oxidants that deal with toxic elements from our environments, including glutathione.
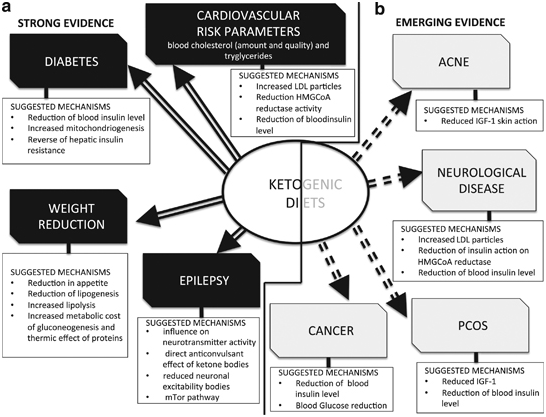
Mitochondria from the hippocampus of ketogenic diet-fed animals are also resistant to mtDNA damage and are much less likely to commit cell suicide—apoptosis—at inappropriate times.
As Douglas C. Wallace, PhD, Director of the Center for Mitochondrial and Epigenomic Medicine says, "the ketogenic diet may act at multiple levels: It may decrease excitatory neuronal activity, increase the expression of bioenergetic genes, increase mitochondrial biogenesis and oxidative energy production, and increase mitochondrial NADPH production, thus decreasing mitochondrial oxidative stress."[21]
Keto-adaptation results in marked changes in how we construct and maintain optimum membrane ("mem-brain") composition, not only because of the healthy fats we provide through the diet, but also because of less free radical production and inflammatory mediators, along with more production of anti-oxidants. It is really the ideal balanced state.
Moreover, you might want to keep in mind this excerpt from "Human Brain Evolution: The Influence of Freshwater and Marine Food Resources"[22]:
There are two key advantages to having ketone bodies as the main alternative fuel to glucose for the human brain.
-
- First, humans normally have significant body fat stores, so there is an abundant supply of fatty acids to make ketones.
- Second, using ketones to meet part of the brain's energy requirement when food availability is intermittent frees up some glucose for other uses and greatly reduces both the risk of detrimental muscle breakdown during glucose synthesis, as well as compromised function of other cells dependent on glucose, that is, red blood cells.
One interesting attribute of ketone uptake by the brain is that it is four to five times faster in newborns and infants than in adults. Hence, in a sense, the efficient use of ketones by the infant brain means that it arguably has a better fuel reserve than the adult brain. Although the role of ketones as a fuel reserve is important, in infants, they are more than just a reserve brain fuel—they are also the main substrate for brain lipid synthesis.
I have hypothesized that evolution of a greater capacity to make ketones coevolved with human brain expansion. This increasing capacity was directly linked to evolving fatty acid reserves in body fat stores during fetal and neonatal development. To both expand brain size and increase its sophistication so remarkably would have required a reliable and copious energy supply for a very long period of time, probably at least a million, if not two million, years. Initially, and up to a point, the energy needs of a somewhat larger hominin brain could be met by glucose and short-term glucose reserves such as glycogen and glucose synthesis from amino acids. As hominins slowly began to evolve larger brains after having acquired a more secure and abundant food supply, further brain expansion would have depended on evolving significant fat stores and having reliable and rapid access to the fuel in those fat stores. Fat stores were necessary but were still not sufficient without a coincident increase in the capacity for ketogenesis. This unique combination of outstanding fuel store in body fat as well as rapid and abundant availability of ketones as a brain fuel that could seamlessly replace glucose was the key fuel reserve for expanding the hominin brain, a reserve that was apparently not available to other land-based mammals, including nonhuman primates.
It is indisputable that a ketogenic diet has protective effects in our brains. With all the evidence of its efficacy in mitochondrial dysfunction, it can be applied for all of us living in a highly stressful and toxic environment. Ketone bodies are healing bodies that helped us evolve and nowadays our mitochondria are busted in some way or another since the odds in this toxic world are against us. Obviously, there are going to be people with such damaged mtDNA or with mutations they were born with, who can't modify their systems (i.e. defects on L-carnitine metabolism), but even in some of those cases, they can halt or slow down further damage. Our healthy ancestors never had to deal with the levels of toxicity that we live nowadays and nevertheless, they ate optimally. Considering our current time and environment, the least we can do is eat optimally for our physiology.
The way to have healing ketone bodies circulating in our blood stream is to do a high fat, restricted carb and moderated protein diet. Coupled with intermittent fasting which will enhance the production of ketone bodies, and resistance training which will create mitochondria with healthier mtDNA, we can beat the odds against us.
What is considered nowadays a "normal diet" is actually an aberration based on the corruption of science which benefits Big Agra and Big Pharma. If we would go back in time to the days before the modern diet became normalized by corporative and agricultural interests, we will find that ketosis was the normal metabolic state. Today's human metabolic state is aberrant. It is time to change that.
Reference: [1] A research member of sott.net's forum has diabetes type 1 and is doing the ketogenic diet. On normal circumstances, diabetics (including type I) report amazing results on a low-carbohydrate diet. See Dr. Bernstein's Diabetics Solution by Richard K. Bernstein, MD (Little, Brown and Company: 2007). [2] It varies among each person, but the general range is between 0 and 70 grams of carbs plus moderate intake of protein, between 0.8 and 1.5 grams of protein per kg of ideal body weight. Pregnant women and children should not have their protein restricted. [3] Ketogenic diets in seizure control and neurologic disorders by Eric Kossoff, MD, Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, Maryland. The Art and Science of Low Carbohydrate Living by Jeff S. Volek, PhD, Rd and Stephen D. Phinney, MD, PhD. Beyond Obesity, LLC , 2011. [4]A Paoli, A Rubini, J S Volek and K A Grimaldi. Beyond weight loss: a review of the therapeutic uses of very-low-carbohydrate (ketogenic) diets. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2013) 67, 789–796 [5] Rainer J Klement, Ulrike Kämmerer. Is there a role for carbohydrate restriction in the treatment and prevention of cancer? Nutr Metab (Lond). Oct 26, 2011; 8: 75. [6] If the genetic code is the hardware for life, the epigenetic code is software that determines how the hardware behaves. [7] David N. Ruskin and Susan A. Masino, The Nervous System and Metabolic Dysregulation: Emerging Evidence Converges on Ketogenic Diet Therapy. Front Neurosci. 2012; 6: 33. [8] Finkel T, Hwang PM. The Krebs cycle meets the cell cycle: mitochondria and the G1-S transition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jul 21;106(29):11825-6. [9] Matthews C.M. Nurturing your divine feminine. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2011 July; 24(3):248. [10] Hipkiss AR. Energy metabolism, altered proteins, sirtuins and ageing: converging mechanisms? Biogerontology. 2008 Feb;9(1):49-55. [11] Saffran HA, Pare JM, Corcoran JA, et al. Herpes simplex virus eliminates host mitochondrial DNA. EMBO Rep. 2007 Feb;8(2):188-93. [12] Porcellini E, Carbone I, et al. Alzheimer's disease gene signature says: beware of brain viral infections. Immun Ageing. 2010 Dec 14;7:16. [13] Gasior M, Rogawski MA, Hartman AL. Neuroprotective and disease-modifying effects of the ketogenic diet. Behav Pharmacol. 2006 Sep;17(5-6):431-9. [14] Maalouf M, Rho JM, Mattson MP. The neuroprotective properties of calorie restriction, the ketogenic diet, and ketone bodies. Brain Res Rev. 2009 Mar;59(2):293-315. [15] Nylen K, Velazquez JL. The effects of a ketogenic diet on ATP concentrations and the number of hippocampal mitochondria in Aldh5a1(-/-) mice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Mar;1790(3):208-12. [16] Bough K. Energy metabolism as part of the anticonvulsant mechanism of the ketogenic diet. Epilepsia. 2008 Nov;49 Suppl 8:91-3. [17] Finn PF, Dice JF. Ketone bodies stimulate chaperone-mediated autophagy. J Biol Chem. 2005 Jul 8;280(27):25864-70. [18] Yuk JM, Yoshimori T, Jo EK. Autophagy and bacterial infectious diseases. Exp Mol Med. 2012 Feb 29;44(2):99-108. [19] Chandra Wickramasinghe, Milton Wainwright & Jayant Narlika. SARS – a clue to its origins? The Lancet, vol. 361, May 23, 2003, pp 1832. [20] Yordy B, Iwasaki A. Autophagy in the control and pathogenesis of viral infection. Curr Opin Virol. 2011 Sep;1(3):196-203. [21] Douglas C. Wallace, Weiwei Fan, and Vincent Procaccio. Mitochondrial Energetics and Therapeutics Annu Rev Pathol. 2010; 5: 297–348.[22] Stephen Cunnane, Kathlyn Stewart. Human Brain Evolution: The Influence of Freshwater and Marine Food Resources. June 2010, Wiley-Blackwell.
MITOCHONDRIAL FUNCTION DETERMINES CANCER
GROWTH & REPRESSION
To clarify even further, cancer cells burn glucose, an inherently "dirty" fuel as it generates far more reactive oxygen species (ROS) than fat and ketones. But in order to burn ketones, the cell must be healthy and normal. Cancer cells cannot burn fat, and this is the heart of successful cancer treatment, and why ketogenic diets appear to be so effective. They essentially starve the cancer, while nourishing healthy cells.
"The clincher with this theory is that once there's enough mitochondrial damage — it's called a retrograde response or epigenetic signal to the nucleus — once this happens, you start to see the genomic instability. You start to see the accumulation of mutations. So the whole crux of this theory is, which comes first?
The argument in the metabolic theory is that this mitochondrial damage happens first, and then you see the mutations. The mutations appeared [to be] the cause, but in fact they're a downstream signal from the true cause. So you can see why researchers were led on this wild goose chase, trying to find what these mutations were and why they were important," Travis says.
Seyfried has done a remarkable job of compiling supporting evidence for the metabolic theory of cancer. For example, he dug up so-called nuclear transfer studies, most of which date back to the 1980s. They were very simple, elegant experiments in which they took the nucleus of a cancer cell and put it into a normal cell with its nucleus removed. The cells are then grown in a petri dish, after which they're injected into mice, to see what happens.
What they discovered was that when you take the nucleus of a cancer cell, put it in a normal cell, and put it in mice, nothing happens. No cancers develop, and the cells revert back to normal. This despite the fact that you have just inserted cells that have all the driving mutations purported to cause cancer! So why don't you get cancer?
At the time, all they could say was that something in the cytoplasm suppresses cancer. The experiment was then flipped, and when the nucleus of a normal cell was put into a cancer cell, which was then injected into mice, about 98 percent of the animals developed cancer. This is irrefutable evidence that something in the cytoplasm is not only repressing cancer, but is driving cancer too.
"When I interviewed the top guys in the field (I won't say who they are) and asked them about these nuclear transfer experiments, they didn't know about them, for one thing. When I explained it to them, they said, 'Well, if those are true, they're going to turn cancer biology on its head.' But they just hadn't been exposed to thesedata yet.
It's incredible. Thomas N. Seyfried PhD, Professor, Boston College did an incredible job of compiling evidence that builds up. Ketone bodies keep you mitochondria healthy because mitochondria burn ketones without producing reactive oxygen spices. The therapeutic ketosis is a healing process where mitochondria gets rejuvenated and will significantly reduce cancer risk.
It's almost like you're building a case for a murder mystery. There's just so much evidence here and there, and you connect all these dots, the nuclear transfer experiments provide so much compelling data. When you put it all together, it's impossible to deny that this, if not the origin of cancer, it has to be explored further," Travis says.
Reference: The Metabolic Theory of Cancer and the Key to Cancer Prevention and Recovery, February 07, 2016, Dr. Mercola
Can Keto help Cancer? The science behind treatment ~ Dr. Thomas Seyfried, PhD
ANTI-INFLAMMATORY EFFECTS OF A KETOGENIC DIET
Posted on February 23, 2015 by Casey Thaler, B.A., NASM-CPT, FNS
Many are aware that ketogenic diets offer a plethora of health benefits.1,2,3,4,5 Among the ketogenic diet's best properties are its anti-inflammatory effects.6,7 However, despite the emerging popularity of the diet, the scientific community is still relatively uncertain about the exact beneficial mechanisms behind this dietary approach.8,9,10 Recently however, a new study was published which looked at the potential mechanisms underlying the specific anti-inflammatory properties of ketosis.11
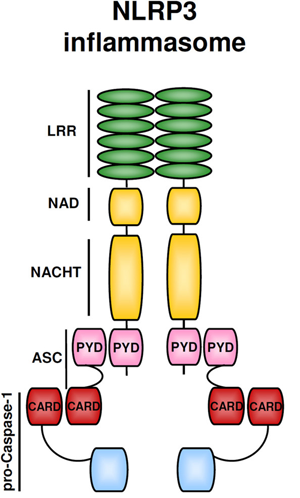
For those unfamiliar, a ketogenic diet is one which contains very little—if any—carbohydrate.12 One classic example of this dietary approach is seen in the Inuit people.13
The Inuit are indigenous people, who live in the Arctic region.14 Alaska, Canada and Greenland all have Inuit populations.15 In one of the more famous nutrition stories of recent times, Dr. Vilhjalmur Stefansson ate nothing but meat for one year, after being inspired by living with the Inuit, and seeing their remarkably low rate of disease.16,17,18 This was despite the Inuit's (then) controversial diet of nothing but meat, whether it came from fish or other sources. Stefansson saw no ill effects from a year of an all meat diet, with basically zero carbohydrate. He also consumed no vegetables. It is worth noting, that he also became very ill when he consumed only low fat meat, and nothing else. When he added the fattier meat back in, he immediately felt better.
The many reported benefits of the ketogenic diet include, but are not limited to: less hunger while dieting, improved cognitive function in those who are cognitively impaired, improved LDL cholesterol levels, improved weight loss, and improved levels of HDL cholesterol.19 This is in addition to the aforementioned anti-inflammatory effects. When we look to the scientific literature, we see that the anti-inflammatory nature of the diet has been studied for many years.20,21,22,23,24 The ketogenic diet has also been established as an adequate anticonvulsant therapy.25
This newly published research looks specifically at the ketone metabolite beta-hydroxybutyrate, which seems to inhibit the NLRP3 inflammasome.26 Since the NLRP3 inflammasome was previously found to have been linked to obesity and inflammation, as well as insulin resistance, inhibiting it would make mechanistic sense.27 The resultant weight loss and anti-inflammatory effects, commonly seem (at least anecdotally) when adopting a ketogenic diet, would then make sense as well. The NLRP3 inflammasome also drives the inflammatory response in several disorders including autoimmune diseases, type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer's disease, atherosclerosis, and autoinflammatory disorders.28,29
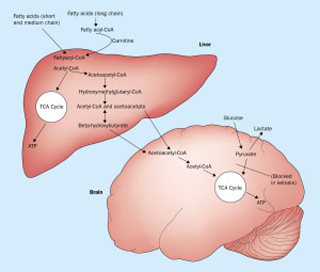
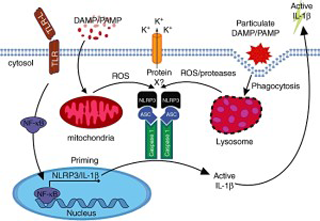
Could it all be so simple? Possibly, though there is certainly likely more to be more scientific discoveries, relating to the beneficial effects of this specific dietary approach. Moving away from glucose and instead utilizing ketone bodies as a source of metabolic fuel, results in many profound changes, of which we are only beginning to scratch the surface of, scientifically.30,31,32
This new discovery will likely be the first of many new findings regarding the ketogenic diet, and its abundance of benefits. If you are looking to adopt a ketogenic approach, simply follow the many nutritious tenets of the Paleo Diet, and then lower your carbohydrate intake to below 100g per day. How low you need to go for optimum quality of life is highly variant, and many people report different results with different amounts of carbohydrates. Dialing in the best nutrition plan for you, when adopting a ketogenic diet, is integral. Be sure to consult with a professional to avoid possible nutrient deficiencies.

Reference: [1] Dashti HM, Mathew TC, Hussein T, et al. Long-term effects of a ketogenic diet in obese patients. Exp Clin Cardiol. 2004;9(3):200-5. [2] Paoli A. Ketogenic diet for obesity: friend or foe?. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2014;11(2):2092-107. [3] Zajac A, Poprzecki S, Maszczyk A, Czuba M, Michalczyk M, Zydek G. The effects of a ketogenic diet on exercise metabolism and physical performance in off-road cyclists. Nutrients. 2014;6(7):2493-508. [4] Hussain TA, Mathew TC, Dashti AA, Asfar S, Al-zaid N, Dashti HM. Effect of low-calorie versus low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet in type 2 diabetes. Nutrition. 2012;28(10):1016-21. [5] Millichap JG, Yee MM. The diet factor in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics. 2012;129(2):330-7. [6] Schugar RC, Crawford PA. Low-carbohydrate ketogenic diets, glucose homeostasis, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2012;15(4):374-80. [7] Masino SA, Kawamura M, Wasser CD, Wasser CA, Pomeroy LT, Ruskin DN. Adenosine, ketogenic diet and epilepsy: the emerging therapeutic relationship between metabolism and brain activity. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2009;7(3):257-68. [8] Poff AM, Ari C, Seyfried TN, D'agostino DP. The ketogenic diet and hyperbaric oxygen therapy prolong survival in mice with systemic metastatic cancer. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(6):e65522. [9] Krilanovich NJ. Benefits of ketogenic diets. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;85(1):238-9. [10] Mandel A, Ballew M, Pina-Garza JE, Stalmasek V, Clemens LH. Medical costs are reduced when children with intractable epilepsy are successfully treated with the ketogenic diet. J Am Diet Assoc 2002;102:396–8. [11] Youm YH, Nguyen KY, Grant RW, et al. The ketone metabolite β-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory disease. Nat Med. 2015; [12] Rogovik AL, Goldman RD. Ketogenic diet for treatment of epilepsy. Can Fam Physician. 2010;56(6):540-2. [13] Phinney SD. Ketogenic diets and physical performance. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2004;1(1):2. [14] Bjerregaard P, Dewailly E, Young TK, et al. Blood pressure among the Inuit (Eskimo) populations in the Arctic. Scand J Public Health. 2003;31(2):92-9. [15] Helgason A, Pálsson G, Pedersen HS, et al. mtDNA variation in Inuit populations of Greenland and Canada: migration history and population structure. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2006;130(1):123-34. [16] Stefansson V: Not by bread alone. The MacMillan Co, NY 1946. Introductions by Eugene F. DuBois, MD, pp ix-xiii; and Earnest Hooton PhD, ScD, pp xv-xvi. [17] McClellan WS, DuBois EF: Clinical calorimetry XLV: Prolonged meat diets with a study of kidney function and ketosis. J Biol Chem 1930, 87:651-68. [18] McClellan WS, Rupp VR, Toscani V: Clinical calorimetry XLVI: prolonged meat diets with a study of the metabolism of nitrogen, calcium, and phosphorus. J Biol Chem 1930, 87:669-80. [19] Pérez-guisado J. [Ketogenic diets: additional benefits to the weight loss and unfounded secondary effects]. Arch Latinoam Nutr. 2008;58(4):323-9. [20] Yang X, Cheng B. Neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory activities of ketogenic diet on MPTP-induced neurotoxicity. J Mol Neurosci. 2010;42(2):145-53. [21] Masino SA, Kawamura M, Wasser CD, Wasser CA, Pomeroy LT, Ruskin DN. Adenosine, ketogenic diet and epilepsy: the emerging therapeutic relationship between metabolism and brain activity. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2009;7(3):257-68. [22] Gasior M, Rogawski MA, Hartman AL. Neuroprotective and disease-modifying effects of the ketogenic diet. Behav Pharmacol. 2006;17(5-6):431-9. [23] Kim do Y, Hao J, Liu R, Turner G, Shi FD, Rho JM. Inflammation-mediated memory dysfunction and effects of a ketogenic diet in a murine model of multiple sclerosis. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(5):e35476. [24] Masino SA, Ruskin DN. Ketogenic diets and pain. J Child Neurol. 2013;28(8):993-1001. [25] Bough KJ, Rho JM. Anticonvulsant mechanisms of the ketogenic diet. Epilepsia. 2007;48(1):43-58. [26] Youm YH, Nguyen KY, Grant RW, et al. The ketone metabolite β-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory disease. Nat Med. 2015; [27] Vandanmagsar B, Youm YH, Ravussin A, et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome instigates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Nat Med. 2011;17(2):179-88. [28] Menu P, Vince JE. The NLRP3 inflammasome in health and disease: the good, the bad and the ugly. Clin Exp Immunol. 2011;166(1):1-15. [29] Zhou R, Yazdi AS, Menu P, Tschopp J. A role for mitochondria in NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nature. 2011;469(7329):221-5. [30] Guzmán M, Blázquez C. Ketone body synthesis in the brain: possible neuroprotective effects. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2004;70(3):287-92. [31] Laffel L. Ketone bodies: a review of physiology, pathophysiology and application of monitoring to diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 1999;15(6):412-26. [32] Henderson ST. Ketone bodies as a therapeutic for Alzheimer's disease. Neurotherapeutics. 2008;5(3):470-80
FIGHT CANCER WITH A KETOGENIC DIET: The Complete Picture
by Ellen Davis, MS
When you view the complete picture, a ketogenic diet has a sort of domino effect on cancer. It lowers average blood-sugar levels, which reduces insulin levels in the blood. Reducing insulin levels effectively inhibits the production of other cancer-promoting downstream factors such as TAF (tumor angiogenesis factor). In addition, higher blood-ketone levels seem to protect normal cells and push cancer cells toward a more normal genetic expression, which means they are more likely to die, as all damaged cells should. To top it all off, low blood-glucose and high blood levels of Beta-Hydroxybutyrate .(BOHB) inhibit the ability of cancer cells to withstand and repair free-radical damage, and finally, ketones can affect cellular gene expression to suppress cancerous behavior. All of these effects compromise a cancer cell's ability to survive. The protective effect of nutritional ketosis is why calorie restriction, fasting, and ketogenic diets (which produce ketones and mimic fasting without the hunger) have such beneficial effects on human health. In fact, nutritional ketosis and ketone bodies themselves are being studied extensively as a treatment for many metabolic diseases.
A growing number of research papers have been published on ketogenic diets and the anti-inflammatory effect of ketone bodies on conditions such as epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, head trauma, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, autism, migraine headaches, stroke, depression, acne, and, of course, cancer.
In fact, this ability of the body to switch fuel sources from glucose to ketones (i.e., to enter nutritional ketosis) is a crucial adaptation that has most likely permitted our continued survival on planet Earth. Ketone bodies act as a backup system when blood-glucose levels fall as a result of either starvation or carbohydrate restriction. Without this adaptation, the human race, from Paleolithic man to the modern cast- away, might have perished during times when food was in short supply.
This is all rather technical, so I'll end this section with the quick summation: to fight cancer metabolically, it is crucial that you lower blood-glucose and insulin levels and increase circulating ketone bodies.
And that is exactly what a ketogenic diet does.
Reference: Fight Cancer with a Ketogenic Diet, Third Edition: Using a Low-Carb, Fat-Burning Diet as Metabolic Therapy 3rd Edition by Ellen Davis, MS
How the Ketogenic Diet Weakens Cancer Cells
BRAIN-GUT-MICROBIOTA AXIS IN PARKINSON'S DISEASE
Introduction Parkinson's disease (PD) is a multicentric neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the accumulation and aggregation of alfa-synuclein (α-syn) in the substantia nigra in the central nervous system (CNS) and in other neural structures. The classical motor symptoms like bradykinesia, resting tremor, rigidity and late postural instability result from the death of dopamine-generating cells in the substantia nigra. There is also a wide spectrum of non-motor manifestations involving for example olfactory (loss of smell), gastrointestinal (GI), cardiovascular, and urogenital systems. It has become evident that the different levels of the brain-gut axis including the autonomic nervous system (ANS) and the enteric nervous system (ENS) may be affected in PD. Recently, it has been also recognized that the brain-gut axis interactions may be essentially influenced by the gut microbiota. On the one hand, dysregulation of the brain-gut-microbiota axis in PD may result in GI dysfunction, which is present in over 80% of PD subjects. On the other hand, this dysregulation may also significantly contribute to the pathogenesis of PD itself, supporting the hypothesis that the pathological process is spread from the gut to the brain.
Conclusion: A better understanding of the brain-gut-microbiota axis interactions should bring a new insight in the pathophysiology of PD, permit an earlier diagnosis with a focus on peripheral biomarkers within the ENS, as well as lead to novel therapeutic options in PD. Dietary or pharmacological interventions should be aimed at modifying the gut microbiota composition and enhancing the intestinal epithelial barrier integrity in PD patients or subjects at higher risk for the disease. This could influence the initial step of the following cascade of neurodegeneration in PD. The elucidation of the temporal and casual relationship between the gut microbiota alterations and the pathogenesis of PD will be of great clinical relevance. Further studies on a new therapeutic approach in PD based on the modification of the gut microbiota with probiotics, prebiotics, or even fecal microbiota transplantation are awaited.
[ Read complete article ]
A gut (microbiome) feeling about stress and brain development ~ John Cryan
The Many Facets of Keto-Adaptation: Health, Performance, and Beyond
Ketosis Safe Long Term and Intermittent Fasting 4 Videos
Dr. Zach Bush M.D. 4 Videos
Low-fat versus Ketogenic diet in Parkinson's disease: A pilot randomized controlled trial
It is plausible and safe for PD patients to maintain a low-fat or ketogenic diet for 8 weeks. Both diet groups significantly improved in motor and nonmotor symptoms; however, the ketogenic group showed greater improvements in nonmotor symptoms. © 2018 The Authors. Movement Disorders published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Read complete article…Read complete article…
The Awful Results of a Low Cholesterol Diet
The body regulates dietary sugar to 0.1%, but there is no regulator in the bloodstream or anywhere in your body for cholesterol!
What do you think this means? The answer is "IT ISN'T REQUIRED!". However, the body does have sensors to tightly monitor blood sugar, calcium, sodium, etc. The body doesn't monitor cholesterol levels because nature doesn't care what they are because its structure wouuld be correct. If we were eating properly and getting good, natural fats in our diet, there would be no cholesterol problem. It is the man-made, chemically altered fats, and the overly high-carbohydrate diet, that cause the problems.
The Alzheimer's Antidote: Using a Low-Carb,
High-Fat Diet to Fight Alzheimer's Disease,
Memory Loss, and Cognitive Decline
by Amy Berger
The wonderful things cholesterol does for us throughout the body:
- Serves as an essential structural component for cell membranes and plasma membranes
- Serves as an essential structural component of the myelin sheath, which insulates and protects neurons and facilitates communication between them
- Is required for synthesis of all steroid hormones, including testosterone, estrogen, progesterone, aldosterone, cortisol, and more
- Serves as a raw material for endogenous (internal) production of vitamin D, via the interaction of sunlight with our skin
- Is required for proper function of serotonin receptors in the brain
- Serves as an essential component of bile salts, which are required for the digestion of fats and fat-soluble vitamins and phytonutrients
- Serves as a repair substance, needed for repair and regeneration of damaged tissue
With cholesterol serving so many vital functions in our bodies-and in the brain, in particular-imagine what would happen under a long-term deficiency, such as might be induced by a very low-cholesterol diet or statin drugs or other cholesterol-lowering medication.
As Jimmy Moore and Eric Westman, MD, authors of the book Cholesterol Clarity, put it, "The knee-jerk reaction to push a statin medication to lower your cholesterol as the first line of defense without looking further into the cause is one of the most foolish things your doctor could ever do."
As it relates to brain function, myelin is made largely out of cholesterol. If there isn't enough cholesterol in the body to create and maintain this myelin, then neurons will "short out" like ungrounded electrical wires.
You may be surprised to learn that incidents of Heart Disease have increased steadily with the advent of these overly high-carbohydrate diet and low cholesterol recommendations.
The American Death rate from Heart Attack and Stroke was only 3% in 1900. By 1997 it increased to nearly 50% (while eating more grains, less protein, less fat, and less cholesterol)!
It is becoming far too common for young men, even those in their thirties, to be prescribed cholesterol-lowering drugs. Men in this age range, who have been "eating right" for years and taking their prescriptions faithfully, are still dying of heart attacks at an alarming rate.
Rather than seeing an improvement in the state of our nation's health, it has declined dramatically. Why, if all of the recommendations given to us for years are correct, are we getting sicker faster? Why, if we were consuming considerably higher levels of cholesterol in the past were our hearts and vascular systems healthier then than they are now? If the dietary recommendations we've been following were correct, the opposite should be true.
Nina Teicholz at TEDxEast: The Big Fat Surprise
The Dangers of Low Cholesterol
Now that you know some of the valuable things cholesterol does for us, let's look at just a handful of the health problems that can result from cholesterol levels that are too low. The following are all linked to low cholesterol and are also well-documented side effects of statin drugs. (Though I hesitate to call them "side effects" They are not side effects. Because of the mechanism by which statin drugs inhibit internal cholesterol production, these are direct effects of the drugs. They aren't incidental, bystander-type effects but, rather, are unavoidable and obvious consequences of what happens when we deprive our bodies of something as essential and important as cholesterol.)
- Depression: Cholesterol is required for proper functioning of serotonin receptors. Serotonin is one of the "feel good" neurotransmitters that helps promote positive moods. Low serotonin has been linked to depression, "winter blues" and an overall negative outlook.
- Fatigue, muscle pain, and weakness: Recall that statin drugs block production of COQ10, the molecule that is part of the mitochondrial energy generators. The thing to note here is that COQ10 isn't just required for energy production in neurons; it is required in almost every cell in the body! It doesn't take a PhD to hazard a guess as to what might happen if muscle cells can't generate energy. Fatigue, muscle pain, and muscle weakness are completely logical and utterly predictable consequences of COQ10 depletion driven by statin drugs.
- Hormonal imbalances and infertility: Because cholesterol is the raw material from which testosterone, progesterone, and estrogen are produced, insufficient cholesterol can lead to hormonal problems and infertility in both women and men.
- Loss of libido: For the very clear reason stated above-we need cholesterol to synthesize the "sex hormones:' Now you can see why so many older men-who have been advised for decades to decrease consumption of foods rich in cholesterol and are likely also taking statins-require pharmaceutical drugs to get or maintain an erection and boost their sex drive, which has been killed by a lack of cholesterol. (Sex drive can be affected in women, as well.)
- Poor digestion of fats and fat-soluble nutrients: Cholesterol is necessary to produce bile, which helps us break down fats in order to digest and absorb not only the energy in them, but also other compounds that are best absorbed along with fats. These include (among other things) fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) and carotenoids, such as beta-carotene-the orange/yellow pigment in carrots, sweet potatoes, and other similarly colored foods. (So put butter on your sweet potato! Or drizzle olive oil on your roasted carrots! Nutrients in these foods are absorbed better when they're eaten with fat.) Long-term poor digestion and malabsorption of these nutrients can lead to a number of health problems. The old adage "you are what you eat" doesn't tell the whole story. You're not what you eat, but rather, what you digest and absorb.
- Memory loss and poor cognitive function: It should be obvious by now that any disruption in cholesterol or COQ10 synthesis will have dire consequences for cognitive function, to say nothing of the role of statins in inducing blood sugar abnormalities and problems with insulin signaling. The brain cannot work without cholesterol and COQ10. Let me say that again: The brain cannot work without cholesterol and COQ10.
According to Dr. Bredesen, whose MEND program (metabolic enhancement for neurodegeneration) has led to reversals of Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer's Disease (AD):
"People are trying to drive their LDLs so low. We see this all the time, where you have some [brain] atrophy and it's associated with having a very low cholesterol. Why? Because you're on a statin... You're preventing your cells from doing the thing that's actually appropriate, so you end up with a brain that has shrunken without the appropriate lipid content. To explain to people that this is actually not good for your brain is not easy."
I cannot and do not suggest that you discontinue taking any medication on your own, but I give you my strongest urging to speak with your doctor and begin exploring that option if you are taking a statin to reduce cholesterol and are experiencing memory loss, brain fog, or other disturbing changes to your cognition or behavior.
The low-carbohydrate diet advocated in this book will go a long way toward aiding healthy brain function, but progress and improvement will very likely be hindered if cholesterol synthesis is being reduced inside the body.
Reference:
The Alzheimer's Antidote: Using a Low-Carb, High-Fat Diet to Fight Alzheimer's Disease, Memory Loss, and Cognitive Decline
by Amy Berger
The Statin Damage Crisis
"As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.―#CommissionsEarned"
In his conclusions Duane Graveline M.D., M.P.H. in his book "The Statin Damage Crisis" expresses his clear discoveries of how the medical industry has provided us with absolutely wrong information. Please read ahead:
My purpose in the choice of the book title "The Statin Damage Crisis" is to draw attention to the thousands of statin damaged people who have written to me about their disabling neuropathies, myopathies and a variety of neurodegenerative conditions such as ALS and Parkinsonism associated with statin use.
But the crisis is far more than this, for with the multibillion dollar statin drug industry, physicians are rapidly losing the confidence of their patients. The so-called doctor/patient bond has never been stretched so thin.
Denying statin causality, despite obvious highly suggestive temporal relationship and often despite the drug company warnings on the package inserts, has caused much grief. The use of statin drugs in diabetics despite drug company warnings of increased peripheral neuropathy is but one example of medicine gone wrong. Why, I ask myself, do physicians push statin drugs to diabetics when the medical literature clearly states that statin treatment is associated with a sixteen times greater risk of peripheral neuropathy.
The thousands of complaints from patients suffering from aches and pains, fatigue and weakness, casually dismissed as, "You've got to expect this now that you are over fifty" is another very common example of medicine gone wrong. When did doctors stop listening to their patients?
Many doctors are so out of touch with the reality of statin side effects they cannot counsel rationally. They know only what was told to them 15 years ago, "Statins may cause a few aches and pains or liver irritation that goes away when the dose is lowered." That is all they know.
Of the thousands of post-marketing MedWatch Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) they largely know nothing. I have personally documented that thousands of amnesia episodes, reported via MedWatch to the FDA, remain unreported to the medical community and the average doctor is shocked into disbelief when told the truth. This is a major crisis.
Another crisis is the policy of the insurance industry to use cholesterol levels as a reason to either deny health care coverage or life insurance coverage, or to extract higher premiums. Some employers even require cholesterol levels to be below a certain number as a condition of employment. Then there is the crisis of patients being forced into taking a statin because not to do so would result in being labeled as non-compliant and facing the prospect of having to find a new doctor. This outmoded concept is based on misinterpreted Framingham data of 40 years ago and cholesterol numbers are increasingly being dismissed as a cardiovascular disease risk factor. Cholesterol level appears irrelevant to the process of atherosclerosis for most people.
Two generations of physicians have been brainwashed with the cholesterol concept of heart attack risk championed by Ancel Keys and his manipulated data. Statin drugs apparently work not by cholesterol reduction but by anti-inflammation. Only relatively recently have we known this. The wheels grind slowly in these agencies and returning truth and reason to these large administrative structures will take much time.
Another crisis, a crisis of confidence, exists for many physicians who follow cholesterol lowering guidelines yet are stunned to find out that most of the people who write these guidelines are in the direct employ of the drug companies. Which is the greater statin damage crisis, the physician who prescribed the statin drug in ignorance of potential side effects, or the physician who prescribes the statin drug with full awareness of the potential for consequences?
But the most important crisis is that of thousands of people disabled by statin associated neuro-muscular problems while thousands of physicians still remain unaware that statins can do this. The statins strike me as being catastrophic in their potential for adversely affecting the human body. It seems like another thalidomide in the making. Imagine, a drug capable not only of subtly allowing excessive oxidation and DNA damage to our mitochondria by inhibiting CoQ10 but also interfering with the daily process of DNA error correction taking place continuously to our mitochondria by simultaneously inhibiting our dolichols. To most clinicians this is meaningless. It was not taught in medical school and most have been much too busy to stay abreast of all that science. When I first read of this in my research it seemed far too complicated for me to understand.
But the principles of this knowledge are very understandable. CoQ10, co-existing as it is in our mitochondria, plays a vital role in preventing excessive oxidation. In so doing it minimizes the formation of the so-called reactive oxygen species (ROS) flashing through our lipid and protein molecules, adding a methyl group here and knocking off another there resulting in completely alien effects if not corrected. And imagine, if you will, a dolichol orchestrated system of specific glycoproteins existing for the sole purpose of correcting this daily load of DNA errors. Statins decrease the bioavailability of both CoQ10 and dolichols. What more do you need to know to be suspicious that mitochondrial mutations are slowly accumulating, robbing us of our important last years?
And this entire black thing is masquerading as premature senility. Is it any wonder doctors, when hearing these patient complaints of tiredness, weakness, wobbly-kneed with burning pain and numbness, poor coordination and terrible memory, respond with a predictable, "You are over fifty now and have to expect these kinds of things." The various processes statins initiate take years to develop. So far the medical community is comfortable with blaming God for these premature disabilities and deaths and turns a deaf ear to these complaints. And I cannot yet prove a thing.
Duane Graveline M.D., M.P.H.
Former USAF Flight Surgeon
Former NASA Astronaut
Retired Family Doctor
For more information on Statin Drugs and their Side Effects,
visit: www.spacedoc.com
The Cholesterol Myth by Dr. Eric Berg, DC 14 Videos
Alzheimer's is called now Type III Diabetes
In his book "Alzheimer's Solved (Condenses Edition)" Henry Lorin presents some conclusions and recommendations in chapter 26. I highly recommend that you read his complete book to understand in detail how he arrives at the following conclusions.
Preventive Dietary Suggestions
Simple dietary changes can prevent or at least manage most of the diseases and conditions discussed in this book. However, do not make changes in your diet without first consulting your personal physician.
The goal is to somehow maintain blood cholesterol levels that will be high enough to keep you in the safe middle area of the cholesterol U.
The easiest and most natural way to do this is by eating foods that contain cholesterol, while minimizing the consumption of foods that are primarily carbohydrates (starches).
Eating foods containing cholesterol will not cause you to have blood cholesterol levels high enough to increase the risks for heart disease. The liver/cholesterol feedback inhibition mechanism will protect against it.
For those readers who believe that some type of plant-derived carbohydrate is absolutely necessary, my response is that the design of humans is such that they can actually do quite well with minimal amounts of starch in the diet. Obtaining glucose (blood sugar) from animal proteins and animal fats through the process of gluconeogenesis is part of the human design.
Some health and medical professionals believe that a diet high in animal protein places extreme stress on the kidneys. However, no real medical research provides a basis for this notion. As long as you drink plenty of water every day, your kidneys will be able to handle all of the animal protein you eat.
What follows is a brief outline of what I believe is a natural dietary plan for humans. It is important to eat sensible portions and perform regular exercise every day.
- Any kind of meat is acceptable
- Also acceptable are eggs, cheeses, milk, yogurt, butter, and ice cream
- Soups made with animal bones are acceptable
- All vegetables are acceptable. However, try and limit consumption of starches, such as potatoes, rice, breads, cakes, donuts, cookies, bagels, nachos, pizza, etc
- Eat fruits with a high sugar content sparingly
Now comes some good news. If you are not obese, engage in moderately vigorous exercise every day, do not smoke, and do not have high blood pressure, you can eat anything you want. It is still important, however, to regularly eat foods containing cholesterol. This is especially important as you enter the senior years.
As far as nutritional supplements are concerned, I recommend taking the following every day: a multivitamin that has all of the trace items, vitamins C and E, calcium (for those who do not like milk), and vitamin D for calcium absorption and help in minimizing cancer risk. There are some brands of orange juice with calcium added, which helps those who cannot swallow large pills.
Death Rate From Alzheimer's Disease Has Risen By 55%, finds the CDC
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have released very startling data about Alzheimer's Disease (AD). The morbidity rate from the neurodegenerative disease posted an astonishing 55% increase between 1999 and 2014. The CDC's Weekly Morbidity and Mortality Report noted that the death rate of people with AD rose from 16.5 to 25.4 deaths per 100,000 during this time.
Symptoms of AD include memory loss, impaired language, confusion, disorientation, and difficulties in decision making.
A fatal form of dementia, AD is now the sixth leading cause of death in the U.S. Almost four percent of deaths in 2014 were attributed to AD which is also one of the top ten causes of death among people ages 65 years and older.
Alzheimer's has tripled among adults ages 30-64, finds Blue Cross
The new report reveals a dramatic increase in Alzheimer's and early-onset dementia, especially among 30-44-year-olds.
Blue Cross has reported a 200% increase in the number of Americans age 30 to 64 diagnosed with early-onset dementia or Alzheimer's disease. The Blue Cross Blue Shield Association recorded the increase between the years 2013 and 2017, among commercially insured Americans, and findings also show that women make up 58% of those diagnosed.
A closer look at the numbers reveals that the increase is particularly dramatic among younger American adults, with a 373% increase in early-onset dementia or Alzheimer's disease among 30 to 44-year-olds. The increase is high across the board, though, with a rise of 311% among 45 to 54-year-olds and 143% among 55 to 64-year-olds.
A gut (microbiome) feeling about stress and brain development ~ John Cryan
The root causes of Alzheimer's disease & how to prevent it
It is possible for those who are struggling with cognitive decline to regain brain function and take back their lives. Despite what the conventional medical model has taught us about cognitive decline and Alzheimer's, these disorders are actually within our power to stop, slow, and reverse.
Remember to eat Sensible Portions
A pure vegetarian diet, with absolutely no foods derived from animals, is not a natural diet for humans, especially as you get older. Can you find a society of people someplace on Earth who all reach the age of 100 or beyond, and yet eat no foods whatsoever that are derived from animals? The answer is no.
If you believe that you may be at risk for one or more of the diseases and conditions in this book, it becomes imperative that you consume foods with cholesterol. The easiest method is by eating eggs every day or almost every day. (Remember to consult your physician before making dietary changes).
I do not know if the amounts of cholesterol obtained from eating eggs change according to the way they are prepared. If there are differences, then it is probably a scale with raw eggs providing the most and hard fried or hard-boiled providing the least amounts of cholesterol. Those eggs softly scrambled, once over lightly, and sunny-side-up are probably somewhere in the middle of the scale.
A quick and easy way to obtain a maximum amount of cholesterol is by drinking eggnog. What follows is my recipe. I prepare this eggnog in the same glass I drink it from, using an electric mixer with a beater blade that reaches down into the glass. I mix it in a very tall glass.
The ingredients are:
- four ounces of whole milk that has vitamins A and D added
- three eggs
- one teaspoon of vanilla extract
- one teaspoon of Bee Honey, and
- a few sprinkles of nutmeg
Mix thoroughly, then drink it. It will usually total up to be about nine ounces in all.
It is a mistake to think that the consumption of eggs is only for their cholesterol contribution. The egg possesses all components necessary for the construction of a warm-blooded vertebrate. The materials in an egg can create skin, muscle, bone, cartilage, brain, nerves, blood vessels, and eyes. These materials are almost exactly the same chemically as those that are found in the human body.
Finally, there are some individuals who believe that the only way to deal with Alzheimer's is through a strategy labeled "prevention through delay." It seems to be based on the premise that some people are destined to develop the disease sooner or later. In this strategy, one follows specified lifestyle, dietary, medication and medical testing recommendations, which supposedly will delay the development of full Alzheimer's disease. This delay then provides time for the patient to die of some other cause before full Alzheimer's symptoms appear.
I do not think this is a good strategy. First, some of this plan's dietary and medication recommendations might actually cause one to develop Alzheimer's sooner, instead of delaying the disease. More importantly, because you have read this book, you now know the true cause of the disease. You are now prepared to prevent Alzheimer's by actually preventing Alzheimer's.
Alzheimer's Antidote & Low Carb Secrets ― Amy Berger 8 Videos
How to fight Alzheimer's disease ― Dr. Bredesen (English/Español)
Mitochondrial Function and Dysfunction
Amy Berger, MS, CNS, NTP
Membranes do not only appear at the outside border of cells. They surround the mini structures called organelles inside the cell as well. The structures we are especially concerned with are the mitochondria (singular = mitochondrion). The mitochondria are the "powerhouses" or energy factories of our cells. They are the sites where energy is produced.
As you can see, mitochondria have both an outer membrane and an inner membrane. And the process of energy production takes place along a system embedded within the inner mitochondrial membrane. The final stop is an enzyme called ATP synthase. (There are thousands of ATP synthases studded along the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Accumulating evidence suggests that mitochondrial dysfunction is intimately associated with AD pathophysiology. ...Mitochondrial dysfunction and the resulting energy deficit trigger the onset of neuronal degeneration and death. ~ Paula L. Moreira and colleagues
ATP is the "energy currency" of the human body: In order to conduct economic business in the United States, we use dollars; in order to conduct physiological and biochemical business, the cells in our bodies use ATP. And if ATP is our energy currency, then think of mitochondria as the mints where the currency is manufactured.
The term mitochondrial dysfunction is being used more and more to describe what underlies neurological degeneration―including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, also known as "Lou Gehrig's disease"), multiple sclerosis, and more! If mitochondria are what literally create energy, then damage to them will result in a cellular energy crisis. And by now, you are coming to understand that Alzheimer's disease is a cellular energy crisis in the brain.
Mitochondria might malfunction for many reasons, including inborn genetic errors and mutations. In this chapter, we will explore glycation and oxidation, two of the most prominent causes of mitochondrial dysfunction over which we can exert an influence. They are both largely the consequences of excessive consumption of the refined carbohydrates and isolated vegetable and seed oils that make up such a large part of the modern diet. You will see that you can keep your mitochondria healthy by adopting a nutrient-dense, reduced-carbohydrate diet, getting adequate sleep, and managing your stress levels. Your mitochondria will also benefit from regular physical activity, whether this means walking, biking, gardening, weightlifting, golf, yoga, pilates, swimming, senior aerobics―whatever you can handle and enjoy. When it comes to your mitochondria, think of the phrase, "Use 'em or lose 'em." Staying active gives the body a reason to generate new, healthy mitochondria. Physical movement―especially higher intensity movement―provides the stimulus the body needs to create more mitochondria, and combined with regular dedication to low-intensity activity (such as walking or gardening), it can keep the ones it has in good working order. Give the body a reason to make and maintain healthy, well-functioning mitochondria, and it will.
Mitochondrion is a double-layered entity. An inner membrane surrounds the inside portion, and an outer membrane encapsulates the mitochondrion as a whole.
In order to more fully understand the nutritional strategy outlined in this book―in particular, the importance of improving insulin sensitivity and blood glucose control and the emphasis on including certain types of dietary fats and avoiding others―it will be helpful for you to become familiar with the terms glycation and oxidation.
Glycation and oxidation are processes that occur in the human body as the result of normal, healthy metabolism. They are consequences of simply being alive, breathing, metabolizing food, and physically moving our bodies. However, glycation and oxidation are supposed to happen at low levels, very slowly, over a long period of time. When they happen more quickly and to a greater degree than normal, they overwhelm the body's capacity to repair the cells and tissues these processes can damage. Out-of-control glycation and oxidative stress are associated with (and might also directly or indirectly cause) many chronic illnesses of our time, including Alzheimer's disease.
Uncontrolled glycation and oxidation in the brain can be thought of as two types of "brain damage" that are part of the vicious cycle of Alzheimer's. This cycle is initiated by glucose- and insulin-handling problems, as well as by an imbalance of fatty acids in the diet. Glycation and oxidation are part of the vicious cycle because metabolic problems with carbohydrate intolerance come first, but once rampant glycation and oxidative stress take hold, they make it even more difficult for neurons to function properly and for communication to occur smoothly between brain cells. Below we will discuss these in more detail, beginning with glycation.
Glycation
Have you ever left a lollipop or hard candy on the dashboard of a car on a hot summer day? What happens? The sugar melts, spreads all over the nearby surface, and makes everything sticky and almost impossible to clean. And when the sugar hardens and dries, it solidifies and becomes almost as brittle as glass.
Something similar happens inside the body when we have a large amount of sugar (glucose) in our blood for extended periods of time. The medical term "hemoglobin Ale," which we've already discussed, refers to hemoglobin (the protein that carries oxygen in the blood) that has become sticky with sugar. It is glycated hemoglobin. Glycation is a function of glucose exposure and time―that is, the greater the amount of glucose in the blood, and the longer the high blood sugar is sustained, the more glycation will occur throughout the body.
Diabetics with poorly controlled blood glucose typically have elevated Alc values because their blood sugar is almost always a little higher than is healthy. (You might recall from chapter 2 that hemoglobin Alc is an approximate average of the blood glucose level during the previous three months or so.) And when Alc is elevated, think of it like the blood being sticky and gunky. Its consistency or viscosity has gone from watery to more like maple syrup or molasses, and when the blood is thicker, it doesn't flow as smoothly as healthy blood. This can lead to a number of problems resulting from poor delivery of oxygen and nutrients from the blood to the tissues that need it.
Hemoglobin isn't the only thing in the body that can become glycated. Almost any structure inside us can suffer this fate of getting mucked up and sticky with sugar, including the structural proteins that make up the arteries, capillaries, and other blood vessels. Healthy blood vessels are like soft rubber hoses that are very accommodating―meaning, they can readily dilate and expand in order to easily accommodate blood flow. In contrast, blood vessels that are glycated become hard and unyielding, acting more like glass tubes―brittle and fragile. So when blood glucose is chronically high, instead of water flowing through a nice rubbery hose, we have some- thing akin to thick, dense molasses being forced through a brittle glass tube that is less able to expand and accommodate the volume of blood. Think how much harder the heart needs to work in order to pump blood through this smaller space, and how much harder the blood will press up against the blood vessel walls. This might contribute to high blood pressure (hyper- tension), which is very common in individuals with type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance. Hypertension is one of the defining diagnostic criteria for metabolic syndrome, and chronically high insulin levels are a likely culprit behind essential and idiopathic hypertension. (It is also why high blood pressure very often resolves upon adopting a low-carb diet.)
The logical and almost inevitable outcome of compromised blood vessel health and vessel dysfunction secondary to chronically high blood glucose and insulin is the high incidence of the various cardiovascular complications many people with diabetes experience that go far beyond hypertension: heart attack, burst blood vessels in the eyes, poor circulation, kidney failure (due to damage to the tiny blood vessels involved in filtering blood), loss of feeling in the extremities (diabetic neuropathy), and more.
The consequences of blood sugar and insulin dysregulation on the cardiovascular system are devastating. Now consider the effects that might take place in the brain. Brain cells can become glycated (just like the car dashboard), and if they become covered in sticky sugar or sugar that is hardened and fragile like glass, these cells will cease to function properly. Glycation is one of the connections between abnormal blood glucose and insulin levels and damage to the brain.
But the damage glycation causes doesn't stop there. Sometimes, glycated structures connect (or bond) with each other, forming larger groups of harder and stickier cells and tissues, called "advanced glycation end-products", commonly referred to by the not-ironic acronym "AGEs." In fact, glycation of proteins in the skin might contribute, in part, to the visible signs of aging, such as dry and brittle skin, sagging skin, and lines and wrinkles. But what happens to the skin on the outside is nothing compared to what happens to the brain on the inside.
According to researcher Stephanie Seneff and colleagues,
"With increased exposure to glucose, multiple proteins in both astrocytes and neurons are susceptible to glycation damage. A glycated protein suffers from a loss of function, increased susceptibility to oxidative damage, and increased resistance to degradation and disposal."
Another way to think of AGEs is like charred or blackened meat. Think of the dark crust that forms on the surface of meat when you grill or sear it―that is also an advanced glycation end-product. The health consequences of consuming AGEs in our foods are quite different from when they form inside our bodies, but it is still a helpful image for us to use to think about the damage or "burning" that occurs when AGEs form inside the brain:
- Sticky, damaged cells
- Cells that are no longer capable of transmitting nerve impulses
- Cells whose damage prevents access to long- and short-term memory
- Cells whose damage interferes with proper behavior and impulse control
- Cells whose damage results in the signs of Alzheimer's disease
Oxidative Damage
The other major form of what we can think of as "brain damage" in the Alzheimer's sufferer is oxidative damage, also called oxidative stress, or simply oxidation. Like glycation, a low level of oxidation is a normal, unavoidable consequence of healthy human metabolic processes. It is only uncontrolled, chronic, overwhelming, and unrelenting oxidation that contributes to cognitive decline in the Alzheimer's brain, and there are many different things that can lead to this uncontrolled oxidative stress. The two most relevant and most easily modifiable factors are poor diet and chronic stress (including insufficient sleep).
If you read health publications or follow health stories on the TV news, you have probably heard the term free radicals. It is beyond the scope of this book to delve deeply into the science of what these are; for our purposes, we can think of free radicals as being pinballs inside our cells: They bang around and crash into things. What are these "pinballs" inside us? Technically speaking, these free radicals are "reactive oxygen species" or ROS. Biochemically, they are molecules with unpaired electrons. Molecules with unpaired electrons are unstable, so they will "steal" electrons from somewhere else in order to remedy this unpaired situation. This leaves another molecule with an unpaired electron, and on and on, in a kind of chain reaction. Among the places ROS steal electrons from are the fatty acids that make up cell membranes. When a molecule loses an electron, it is said to be oxidized. And when fatty acids experience this, the damage is called oxidation. In looking to repair this damage, whatever was oxidized (hit by the pinball) tries to steal resources from some other place, resulting in the aforementioned chain reaction of oxidation. The nutrients called antioxidants are helpful for limiting this damage and sometimes preventing it from occurring at all.
So where do the free radical pinballs that wreak havoc as they knock around from cell to cell and structure to structure come from? One source of them is vegetable oils, which are rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids. (Examples include soybean, corn, cottonseed, and safflower oils.) When exposed to heat, light, or air, polyunsaturated fats oxidize, creating ROS that we then consume upon eating foods that contain these oils or were cooked in them.
Another source of ROS is everyday human metabolism. At a cellular level, the mitochondria (remember, these are the mini furnaces that create energy inside our cells) create ROS. We have natural, "in house" antioxidants generated by our own bodies (most notably glutathione and superoxide dismutase) that are designed to limit the damage caused by these ROS, but when too many ROS leak out, they can overwhelm the body's natural antioxidant capacity, leading to greater amounts of oxidative damage. The creation of ROS during energy production is a normal and unavoidable occurrence, but it happens to a larger and more overwhelming degree when the body is trying to create energy from glucose than when producing it from fat. As alluded to earlier, fats are a more efficient and "cleaner burning" fuel than glucose. The generation of energy (ATP) from glucose and fatty acids is slightly different on a molecular level, and this slight difference is enough to account for a greater amount of damaging free radicals generated by the metabolism of glucose.
As for how this affects cognitive function, according to researcher Paula Moreira and colleagues,
"If the amount of free radical species produced overwhelms the neuronal capacity to neutralize them, oxidative stress occurs, followed by mitochondrial dysfunction and neuronal damage."
Transitioning the body from the constant burning of carbohydrate to a fat-based metabolism instead is one way to reduce the oxidative burden in the body and brain.
Considering the important role of antioxidants in limiting the extent of oxidative stress, you might be thinking that high doses of antioxidant nutrients would be beneficial. Indeed, there might be a role for increasing the antioxidant pool in the body, but supraphysiologic doses of antioxidants are not recommended. Oxidation isn't all bad; it's a normal and necessary part of human physiology. In fact, oxidation is one of the tools the immune system uses to neutralize invading pathogens: Cells involved in the immune response oxidize pathogens, thereby killing them or tagging them for removal or excretion. Oxidation is also involved in a process called apoptosis, which is a kind of programmed "cell suicide" or cellular self-destruct mode. This is one way the body has of dismantling and disassembling old, worn out, or malfunctioning cells that are supposed to be gotten rid of. (Cancer cells evade apoptosis, which is why they continue to grow and spread, even though they are not functioning properly.) So while it's important to have an adequate pool of antioxidants to keep oxidative damage from overwhelming the body's tissues, inundating the body with massive doses of antioxidants might actually be detrimental because it could interfere with this critical balancing act. A sensible way to introduce more antioxidants into the body is by consuming foods that are rich in antioxidant nutrients. Many of the vegetables and low-glycemic fruits permitted on a very low-carbohydrate diet fit this bill, as do most herbs and spices, such as turmeric, rosemary, basil, garlic, oregano, allspice, and thyme. Liberal use of these in cooking is encouraged; it is highly unlikely that you would "overdo" antioxidants from food sources.
The brain is more susceptible to oxidative damage than any other major organ because of its high oxygen consumption. Neurons are particularly vulnerable to oxidative stress because their metabolic rate is about five times that of other brain cells. In addition, neurons contain a high proportion of polyunsaturated fatty acids that can interact with ROS to set off a self-propagating chain of lipid peroxidation and molecular breakdown. ~ Mortimer Mamelak
Mitochondrial Mayhem
Being the powerhouses that generate energy for us, mitochondria are both a source and a target for free radicals. In fact, owing to the fragile polyunsaturated fatty acids that are such a large part of the structure of the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes, these tiny generators are especially susceptible to oxidative stress. Just think of the burden they face in light of our modern diet: high in refined sugars and grains, and high in ROS-forming vegetable oils. They become glycated and also suffer constant blows from oxidation. They get a double whammy.
Mitochondrial dysfunction is a major problem in Alzheimer's disease. Mitochondria quite literally produce most of our energy. If they are damaged or reduced in number, it will clearly result in less energy produced in the whole body and, obviously, in the brain. Alzheimer's is a sort of "perfect storm" situation in which brain mitochondrial glycation and oxidation have combined to do serious damage to neuronal health and cognitive function.
It is crucial to protect the mitochondria by limiting the amount of damage that occurs in the first place and also by providing helpful nutrients to clean up and clear away the normal amount of damage that is unavoidable, inevitable, and natural. This is true for healthy people, but it is even more imperative for the Alzheimer's sufferer. The Alzheimer's brain has been suffering the effects of rampant oxidation and glycation for years, sometimes decades. The more quickly and effectively the damage is cleared away, the more quickly the Alzheimer's patient's cognitive function might improve. This is why the powerful nutritional strategy in this book is advised and also why specific supplements are suggested as adjuncts to the diet. This is no time for half-measures. This is the time for a drastic intervention in a race against time. We are trying to preserve and possibly restore healthy cognitive function, in part by restoring mitochondrial health.
One way oxidative damage causes a breakdown in healthy cognition is by changing the shape of the neurons themselves. As discussed in chapter 3, neurons are covered in myelin, which is primarily made up of cholesterol and fatty acids. If we consume too much of the wrong types of fat, these oxidized fats will be incorporated into the myelin structure, and the myelin will not function properly―leading to a breakdown in cellular communication and transmission of nerve impulses between neurons, which is one of the causes of memory loss and poor cognitive function in Alzheimer's. Simply put, the brain cells go "on the fritz" and the logical results are cognitive impairment, memory loss, and behavioral changes.
The same is true for cell membranes: They are made up of fatty acids, cholesterol, and other materials. If we eat an improper balance of fats in our diet, then too many of the wrong types of fat might be inserted into the cell membranes, which will become oxidized, and again, cellular function will be compromised.
To get a true appreciation for why this is so important and for why an alteration in the structure and function of something as seemingly inconsequential as cell membranes holds so much influence over all aspects of health―including cognitive function―let's keep in mind what cell membranes do. Remember, cell membranes are the bouncers of the cell: They allow the good things in and send the bad things out, and they also help cells retain their proper shape. Alter the shape of a neuron, alter its function.
Half of All Children Will Be Autistic by 2025
Warns Senior Research Scientist at MIT
For over three decades, Stephanie Seneff, PhD, has researched biology and technology, over the years publishing over 170 scholarly peer-reviewed articles. In recent years she has concentrated on the relationship between nutrition and health, tackling such topics as Alzheimer's, autism, and cardiovascular diseases, as well as the impact of nutritional deficiencies and environmental toxins on human health.
At a conference last Thursday, in a special panel discussion about GMOs, she took the audience by surprise when she declared, "At today's rate, by 2025, one in two children will be autistic." She noted that the side effects of autism closely mimic those of glyphosate toxicity, and presented data showing a remarkably consistent correlation between the use of Roundup® on crops (and the creation of Roundup®-ready GMO crop seeds) with rising rates of autism. Children with autism have biomarkers indicative of excessive glyphosate, including zinc and iron deficiency, low serum sulfate, seizures, and mitochondrial disorder.
Other toxic substances may also be autism-inducing. You may recall our story on the CDC whistleblower who revealed the government's deliberate concealment of the link between the MMR vaccine (for measles, mumps, and rubella) and a sharply increased risk of autism, particularly in African American boys. Other studies now show a link between children's exposure to pesticides and autism. Children who live in homes with vinyl floors, which can emit phthalate chemicals, are more likely to have autism. Children whose mothers smoked were also twice as likely to have autism. Research now acknowledges that environmental contaminants such as PCBs, PBDEs, and mercury can alter brain neuron functioning even before a child is born.
Even worse, she notes, additional chemicals in Roundup® are untested because they're classified as "inert," yet according to a 2014 study in BioMed Research International, these chemicals are capable of amplifying the toxic effects of Roundup® hundreds of times over.
Glyphosate is present in unusually high quantities in the breast milk of American mothers, at anywhere from 760 to 1,600 times the allowable limits in European drinking water. Urine testing shows Americans have ten times the glyphosate accumulation as Europeans.
"In my view, the situation is almost beyond repair," Dr. Seneff said after her presentation. "We need to do something drastic."

|

|

|
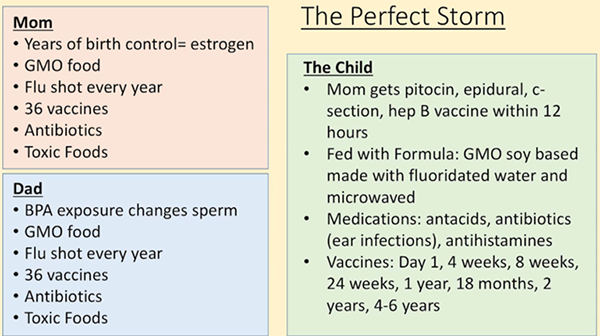
|
|
Heads in the Sand a Case Series: How to deal with "Vaccine Deniers" 3 Videos
WHY IS IT NECESSARY TO KNOW THE SCIENCE?
Unlike our Genome—which we cannot do much about it, except blame our parents and our grand-parents—our Microbiome is readily modifiable.
Conscious Integrative Nutrition is not just a "diet". It is not a method designed just for weight loss, but rather a teaching method whose action provides a healthy and physically toned and lean body.
Today we find many diets to reduce fat ratio, all promising lasting results and each with its particular group of adepts. But, it is obvious that diets do not work, as people with obesity problems are increasing. If diets would work, the problem would be over—there would be no obesity.
There are no miracles without knowledge. Knowledge allows fundamental changes to our habits and beliefs. Start by changing the strategy and use your intelligence. Weight loss is a matter of changing your habits, "change your lifestyle and you will lose weight."
The Gut-Brain Connection by Duke University
Healthy Versus Dangerous Fats
When we're talking about implementing a high-fat diet, it's extremely important to identify which fats we're referring to, and how much.
As a general rule, you'll want at least 50 to 75% of your total calories (some may benefit from as much as 85%) from healthy fats, which include: olives, avocados, coconut oil, MCT oil, organic pastured butter, cacao butter, raw nuts such as macadamia and pecans, seeds such as black sesame, cumin, pumpkin and hemp seeds, organic pastured eggs, grass-fed meats, lard and tallow.
If you're using the fats found in the typical American diet, you're undoubtedly going to get worse, not better. This is actually one of the reasons why the low-fat diet is in fact beneficial for some; because it lowers their intake of harmful polyunsaturated (PUFA) refined vegetable oils, primarily omega-6.
Making matters worse, 85 to 90% of those oils are from corn and soy, most of which are genetically engineered (GE), which means they're more heavily contaminated with glyphosate residues from Roundup®. I suspect glyphosate may be an important contributor to mitochondrial dysfunction.
Reference: The Clinical Use of Nutritional Ketosis, August 14, 2016 mercola.com
The Cure for 97% of Diseases by Dr. Bergman 100 Videos
Monosodium Glutamic Acid (MSG)
Monosodium Glutamic Acid (MSG) refers to a chemical process in which glutamic acid is isolated, and then, bound to a sodium molecule and purified into a white powder that is added to foods as a flavor enhancer. MSG can be an excitotoxin, which means it amps up and stimulates sensory nerves – in an enhanced, tastier way. As a flavor enhancer, the active forms of MSG or glutamic acid are called D-glutamic acid and L-glutamic acid, plus other toxic by-products.
How To Avoid Non-Labeled MSG
Without a doubt we should be reading labels and avoiding any food with MSG in it. Even if you do not seem to be sensitive to it, MSG is an irritant or neurotoxin and can damage the intestinal wall over time and create other problems down the road.
To avoid the non-labeled MSG that is used in very small quantities as a processing aid, all processed foods must be avoided. This includes many health foods such veggies burgers, turkey sausages, textured or hydrolyzed proteins and processed protein powders.
Some and for sure not all health food companies that go through the trouble of avoiding processed proteins in such a way that avoids the production of excess L-glutamic acid, any D-glutamic acid if possible, and the toxic by-products.
The key is to avoid large exposures to MSG and, while being aware of your reaction to all processed foods, especially packed protein products and even protein powders, always choose fresh, non-processed foods as often as possible.
That said, since a small amount of L and D-glutamic acid is incredibly hard to avoid, the most logical thing to do is to continue to support the health of the intestinal skin so that it continues to act as a protective barrier against toxins. If the inner skin breaks down, numerous undigested toxins can enter the blood stream and lymph and become irritants, toxins, allergens and trigger similar symptoms to MSG. Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity is a perfect example.
Hidden names for MSG and free glutamic acid
Names of ingredients that always contain processed free glutamic acid:
- Ajinomoto
- Any "hydrolyzed protein"
- Anything "…protein"
- Anything "hydrolyzed"
- Autolyzed Yeast
- Calcium Caseinate
- Calcium Glutamate (E 623)
- Gelatin
- Glutamate (E 620)
- Glutamic Acid (E 620)
- Magnesium Glutamate (E 625)
- Monoammonium Glutamate (E 624)
- Monopotassium Glutamate (E 622)
- Monosodium Glutamate (E 621)
- Natrium Glutamate
- Sodium Caseinate
- Soy Protein
- Soy Protein Concentrate
- Soy Protein Isolate
- Textured Protein
- Vetsin
- Whey Protein
- Whey Protein Concentrate
- Whey Protein Isolate
- Yeast Extract
- Yeast Food
- Yeast Nutrient
Names of ingredients that often contain or produce processed free glutamic acid:
- Any "flavors" or "flavoring"
- Anything "enzyme modified"
- Anything "fermented"
- Anything "protein fortified"
- Anything "ultra-pasteurized"
- Anything containing "enzymes"
- Barley malt
- Bouillon and broth
- Carrageenan (E 407)
- Citric acid, Citrate (E 330)
- Malt extract
- Maltodextrin
- Pectin (E 440)
- Protease
- Seasonings
- Soy sauce
- Soy sauce extract
- Stock
The following are ingredients suspected of containing or creating sufficient processed free glutamic acid to serve as MSG-reaction triggers in HIGHLY SENSITIVE people:
- Anything labeled "Enriched"
- Anything labeled "Vitamin Enriched"
- Brown rice syrup
- Corn starch
- Corn syrup
- Dextrose
- Lipolyzed butter fat
- Milk powder
- Modified food starch
- Most things labeled "Low Fat" or "No Fat"
- Reduced fat milk (skim; 1%; 2%)
- Rice syrup

Reference: https://lifespa.com/sneaky-names-for-msg-check-your-labels/ http://www.truthinlabeling.org/hiddensources.html
Some improvements after adding Flesh foods to your diet if you have been following "Traditional Vegetarian diet of either All-raw or 80% Raw/20% cooked Therapies"
- Better recovery after exercise—distance runners are able to run hard workouts more frequently with fewer rest days or easy workouts in between
- Better Sleep
- Correction of "visual disturbance" like "spots" in the visual field, obscure vision, which may be developed on the traditional vegetarian diet of either all-raw or 80% raw/20% cooked
- Maintained weight more easily on lesser volumes of food
- Moods improve and more buoyant feelings
- Nervous system becomes more stable and not so prone to hyperreactive panic-attack-like instability
- Not hungry all the time
- Sex drive increases somewhat (usually accompanies better energy levels)
- Stools became a bit more well-formed
Why diets fail?
Starting with the name "Diet". What is needed is not a "diet", more coherent information is needed to help us make the decision to change our "lifestyle", which includes the nutrition of the physical body. Maintaining a vision toward the future, we must recognize the importance of learning coherently, "Give a man a fish, and you feed him for a day; show him how to catch fish, and you feed him for a lifetime."
Lack of Information. The constant bombardment of false-data generates confusion. Thus, research and understanding metabolism with an open and critical mind, modulating and considering the individual characteristics, is the way. You will become slim and healthy, and you'll never get fat again. "It's more important to learn what not to eat, than to learn what to eat."
Lack of Nutrients. By understanding metabolism we discover that we need not starve our bodies. We can have foods that our body is actually designed to consume and enjoy eating deliciously.
Lack of Criteria. No one knows your body better than you, so follow your instincts and modulate food that really works for your metabolism. Start your change convinced that you have a clear motivation that will really change your habits.
Lack of Determination and Support. Accept your body as is. Solve your emotional resentment allowing yourself to rediscover your identity. Just feel your internal support, drop the dependence on external opinion and crutches. Be ware that you will face socio-cultural obstacles. You cannot avoid social engagements, parties and meetings. Inevitably, the key is to be consistent even in difficult times.
Lack of Exercise. The body was designed to move where bone structure works in synergy with the muscular system. It is necessary to integrate physical activity to offset for our current sedentary culture. Exercise mobilizes the lymphatic system detoxifying and strengthening muscles, thus generating vital energy. By eating healthy everyday and spending some time doing physical activities, you will see faster and better results.
HOW DO I GET WELL AND RETAIN MY HEALTH?
- Avoiding grains, sugars, GMOs (Genetically Modified Organisms) and Monosodium Glutamic Acid (MSG)
- Connecting with the Sun in Nature to optimize Vitamin D levels and regulate Circadian Rhythms
- Consuming fermented foods, such as Goat Kefir, Goat Yogurt and Sauerkraut
- Cooking only with Ghee or Coconut oil
- Drinking plenty of Pure Water
- Eating Organic foods
- Fallowing a Ketogenic Diet and Intermittent Fasting
- Maintaining a Energy (spiritual) Practice embracing Meditation and Relaxation
- Moving my body each day using Chi Kung and Yoga
- Oil pulling with Coconut oil
- Sleeping deeply, especially during the healing process
THE CONSCIOUS INTEGRATIVE NUTRITION PROGRAM
The program requires your commitment and dedication for 3 months. The process involves a change in the habits and beliefs that are familiar to you, and inherited through generations. The changes proposed in this program are healthy for all family members, and their participation and support is crucial.
It is designed to streamline the immune, metabolic and neuronal systems changing dramatically the method of cells-energy-delivery which reduces the issues that "glucose/insulin" metabolism produces.
KETO-ADAPTATION
Metabolic Benefits Snap Shot:
- Decrease in Triglycerides
- Decreases the Accumulation of Lactate, contributing to better control of pH and respiratory function
- Heartburn Relief
- Improve Insulin Sensitivity, Resistance and Recovery from exercise
- Improvement in Mental Health disorders
- Increase in HDL Cholesterol and Better Heart Disease Risk
- Less Gum and Tooth disease
- Lower Blood Pressure
- Lower Blood-Sugar (glucose) and HbA1c levels
- Lower levels of Inflammation
- Neurological Support and Protection
- Provides a steady and sustained source of fuel for the brain, protecting athletes from hitting the wall
- Reduce of factor associated with Cancer
- Reduction of inappropriate Hunger and Sugar Craving
- Spares Protein from being Oxidized, preserving lean tissue
- Weight loss
ARE YOU KETO-ADAPTED?
Dietary Macronutrient Content or Keto Ratio (KR) refers to the proportion of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. The optimal relationship of macronutrients in our diet can be loosely described as good Fats, Protein, and Carbohydrate. The Ratio must be at least 1.7―which is intense lipolysis―for a meal to be considered ketogenic. Between 1.3 and 1.6 there is already lipolysis.
To calculate your Keto Ratio introduce in the "Keto/Antiketo Calculator" under Fat, Protein and Carbohydrate (CH) in estimated grams or estimated percent the Fat, Protein, and Carbohydrate contents of your typical food serving for a day. In the "Outcome" you will see your Kato Ratio result. The ideal proportion may be 200grs/55% of Fat, 120grs/33% of Protein, and 45grs/12% of Carbohydrates which will give and ideal outcome of 1.747.
KETO/ANTIKETO CALCULATOR
You can convert Cups to Grams using the following website: Food Converter
Currently, this equation is rarely used in nutrition research, which is regrettable since properly calculated KRs reveals interesting patterns of diet effects.
Lipolysis is the process by which fats are broken down in our bodies through enzymes and water, or hydrolysis. Lipolysis occurs in our adipose tissue stores, which are the fatty tissues that cushion and line our bodies and organs. In fact, fats can be thought of simply as stored energy. Fats are ready and available for when our glucose stores run low between meals, and it makes sense for lipolysis to occur as it will facilitate the movement of these stored fats through our bloodstream. Breaking down this "potential energy" into free moving fatty acids can then allow them to be repurposed or expended as fuel! [ Read full article ]
FATS: Fats are a more efficient fuel for our bodies and each meal should contain a sufficient amount of fats. The four main fats to use are:
- Grass-fed butter
- Grass-fed ghee
- Coconut oil
- Olive oil
Other fats and oils that can be included (provided they are the best quality):
- Lard from grass-fed pigs
- Beef tallow from grass-fed livestock
- Duck fat from grass-fed ducks
PROTEIN: Generally comes from a modest serving of animal products:
- Fish (wild)
- Meat from grass-fed livestock
- Eggs from grass-fed chickens
- Whole-milk from grass-fed livestock
- Raw cheeses from grass-fed livestock
- Organ meats from grass-fed livestock
- Soup or bone broth from grass-fed livestock
CARBOHYDRATE: Are mainly sugars and starches that the body breaks down into glucose and fiber that the body uses to feed its cells.
Simple Carbohydrate: Sugar―fruit, fruit juice, table sugar, honey, soft drinks, and other sweets.
Complex Carbohydrate: Starch―bread, cereal, potatoes, pasta, rice, and legumes (dried peas and beans). Fiber―bran, whole-grain foods, raw vegetables and fruit (especially the seeds and skins), legumes, nuts, seeds and popcorn.
Glycogen is the only complex carbohydrate of animal origin. It exists in limited quantities in liver and muscle tissues and acts as a readily available energy source.
Our true need for dietary carbohydrates is small. Should be low, generally between 45 and 75 grs of net carbohydrates per day. Start with a six-month elimination of all grains and beans and non-fermented milk products. This allows the opportunity for significant gut microbiome restoration. Carbohydrate consumption during this time comes from vegetables such as carrots, beets, or parsnips, and a small amount of fruit. These carbohydrates, in addition to the meats and fats and green vegetables, provide you with all the nutrients, fiber, and vitamins that you need.
INCLUDES
- 1 preliminary session
- 1 cooking class to guide you in the preparation of:
- Fermented Foods
- Vegetable and Animal Cooking oils
- 1 class on the Biology of Human Metabolism
- 1 Yoga series designed for you
- 1 Physical Exercised routine designed for you
- 1 Meditation sequence designed for you
- Nutritional guide listing recommended, acceptable and prohibited foods
The program meets the need for three (3) groups:
| 1. | Individual: | One person | ||
| 2. | A couple: | Two people | ||
| 3. | Family: | A couple with children |
IF YOU'VE DECIDED TO TAKE CONTROL OF YOUR HEALTH!

Subscribe for the preliminary session of the program and contact us to define your goals and objectives.
The preliminary session consists of an interview to assess your current health condition, define the necessary personalized changes to define your custom program.
Please reserve the preliminary session to receive a "Information Document" ![]() in PDF format via email, which will be used as the basis for this program. The full document and a full body photo are required for the preliminary session which will be held personally in Costa Rica.
in PDF format via email, which will be used as the basis for this program. The full document and a full body photo are required for the preliminary session which will be held personally in Costa Rica.
Preliminary Sessions one-on-one at location. Book preliminary session (≈1.5 hours):
$90 USD |
|
Cedit Card (PayPal) |
R.S.V.P.
Info@iChiKung.com to schedule session
Refunds will not be available for registrants who choose not to complete the session.
Disclaimer: Please remember that One-on-One sessions in person or distant healing are not a substitute for professional care or psychiatric help if that is what is needed. Many physicians and psychologists recommend meditation in conjunction with standard therapies.
